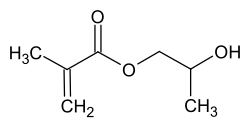
2-hydroxypropyl methacrylate
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
||||||||||||||||
| Structural formula of 2-hydroxypropyl methacrylate | ||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||
| Surname | 2-hydroxypropyl methacrylate | |||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
|||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 7 H 12 O 3 | |||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 144.2 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
liquid |
|||||||||||||||
| density |
1.029 g cm −3 |
|||||||||||||||
| boiling point |
240 ° C |
|||||||||||||||
| Vapor pressure |
130 Pa (65 ° C) |
|||||||||||||||
| solubility |
107 g / l (in water at 20 ° C) |
|||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||||||||
When 2-hydroxypropyl methacrylate (2-HPMA) is an ester of methacrylic acid . It contains both a hydroxyl group and an unsaturated double bond . It is generally used as a monomer for different classes of binders .
properties
When reacting with isocyanates , 2-hydroxypropyl methacrylate has a rather low reactivity. The reason for a rather low reactivity is not a lack of electron-donating effect, but rather a steric hindrance and a low probability of reaction partners encountering the hydroxyl group. It is less reactive than 2-hydroxyethyl acrylate and than 4-hydroxybutyl acrylate . The heat of polymerization is −50.5 kJ mol −1 or −350 kJ kg −1 .
use
2-Hydroxypropyl methacrylate can be incorporated into binders such as polyacrylates via free-radical or ionic polymerization . Since 2-hydroxypropyl methacrylate has a free hydroxyl group, it can be used to build hydroxyl groups into resins. These groups are then available for curing reactions with isocyanates or urea resins .
In addition to the possibility of incorporating 2-hydroxypropyl methacrylate into resins via the double bond , there is also the possibility of doing this via the hydroxyl group. Example would be for this purpose, the reaction of 3 moles of 2-hydroxypropyl methacrylate and one mole of HDI - isocyanurate . This results in a urethane acrylate which can be used as a reactive diluent in coatings that can be cured by means of UV radiation .
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e Entry on 2-hydroxypropyl methacrylate in the GESTIS substance database of the IFA , accessed on June 17, 2018(JavaScript required) .
- ↑ Entry on 2-hydroxypropyl methacrylate in the Classification and Labeling Inventory of the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA), accessed on June 25, 2018. Manufacturers or distributors can expand the harmonized classification and labeling .
- ↑ a b c d Baumstark, Roland, Schwalm, Reinhold, Schwartz, Manfred: Acrylate resins . Vincentz Network, Hannover 2014, ISBN 978-3-86630-820-6 , p. 32; 56; 267; 294 .
- ↑ Brandrup, J .; Immergut, EH; Grulke, EA; Abe, A .; Bloch, DR: Polymer Handbook , 4th Edition, Wiley-VCH 2003, ISBN 978-0-471-47936-9 , p. II / 369.


