Nucleic acid nomenclature
In biochemistry and bioinformatics , nucleic acid nomenclature is used to denote certain abbreviations relating to nucleic acids such as DNA and RNA that have been defined by the IUPAC . The following specifications apply to nucleic acids:
orientation
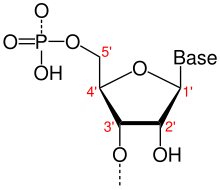
The basic building blocks of a nucleic acid are the nucleotides . Its central element is ribose . The positions in the nucleic acid are described in clockwise direction using the carbon atoms of this molecule . The positions are indicated with the respective number and the ' sign (pronounced dash ). For example, the hydroxyl group at the 2 ′ position of the ribose distinguishes RNA from DNA. The deoxyribose does not have an HO group on 2 ′ .
Since in a nucleic acid the hydroxyl group on 3 'of one nucleobase is connected to the phosphate group of the next, the polarity and thus also the orientation of a DNA strand or an RNA strand is denoted by 5' and 3 ' . For example, polymerases move on the antisense strand from 3 'to 5' , also written 3 '→ 5' . Other enzymes (e.g. some nucleases ), on the other hand, move 5 ′ → 3 ′ , i.e. from the 5 ′ end towards the 3 ′ end. Sense strands are written down 5 '→ 3', corresponding to the reading direction of the ribosomes during translation . This means that the 5 'end is in front and the 3' end is behind . Antisense strands have the opposite direction 3 '→ 5' from the 3'-end towards the 5'-end.
The 3 'and 5' ends also serve to identify the orientation of genes : Sense strands correspond to positive (+), antisense strands to negative (-) polarity .
Symbols of the bases
The five nucleobases of DNA and RNA are abbreviated with their first letters. Further symbols for unspecific nucleobases (two or more nucleobases can be used alternatively) are used if no clear assignment can be made in a sequence.
| symbol | meaning | description |
|---|---|---|
| G | G | Guanine |
| A. | A. | Adenine |
| C. | C. | Cytosine |
| T | T | Thymine |
| U | U | Uracil |
| R. | A or G | Pu r ine |
| Y | C or T | P y rimidine |
| W. | A or T | engl. w eak (weak) hydrogen bonds |
| S. | G or C | engl. s trong (strong) hydrogen bonds |
| M. | A or C | A m inogruppe |
| K | G or T | K etogruppe |
| H | A, C, or T (U) | not G, ( H follows G in the alphabet) |
| B. | G, C, or T (U) | not A, ( B follows A in the alphabet) |
| V | G, A, or C | not T (U), ( V follows U in the alphabet) |
| D. | G, A, or T (U) | not C, ( D follows C in the alphabet) |
| N | G, A, C or T (U) | engl. a n y (all nucleotides possible) |