Adenine
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|

|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Adenine | |||||||||||||||||||||
| other names | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 5 H 5 N 5 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
light yellow solid |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Drug information | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| ATC code | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 135.13 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| boiling point |
Decomposition from 360 ° C |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Sublimation point |
220 ° C |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| solubility |
poor in water (0.5 g l −1 at 20 ° C) |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Toxicological data | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Adenine is one of the four nucleobases in DNA and in RNA , alongside cytosine , guanine and thymine or uracil (in RNA).
It is a heterocyclic organic compound with a purine backbone and an amino group in the 6-position. The deoxyadenosine in DNA and the adenosine in RNA are nucleosides that contain adenine. With thymine or uracil it forms two hydrogen bonds in the Watson-Crick base pairing .
presentation
- Lord Todd synthesis applied to formamidine and phenylazomalononitrile .
- Adenine can be viewed as a pentamer of hydrocyanic acid and can be prepared from it in liquid ammonia with yields of over 20%.
History and biological meaning
On January 12, 1885, the later Nobel Prize winner Albrecht Kossel reported to the Berlin Chemical Society about an important discovery. He was able to isolate a nitrogen-rich base with the empirical formula C 5 H 5 N 5 , for which he derived from the Greek , from a large amount of bovine pancreas, which had been processed by Adolph Bannow (1844-1919) in the Berlin chemical plant Kahlbaum Word "aden" for gland, the name adenine suggested. Kossel also proved it to be a cleavage product of the yeast nuclein. He was later able to detect adenine as a cleavage product of the nucleic acid.
Adenine can be part of DNA, RNA or various nucleosides and nucleotides .
Nucleosides
Via the N 9 atom of the five-membered ring, adenine can be bound N -glycosidically to the C 1 atom of the ribose ; one then speaks of a nucleoside , the adenosine . When binding to deoxyribose , the nucleoside deoxyadenosine is formed . In contrast to most nucleosides, the synthetic vidarabine contains arabinose instead of ribose .
Nucleotides
Phosphoric acid can be bound to adenosine as a phosphate residue, which is how it is formed
- Adenosine monophosphate (AMP)
- Cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP)
- Adenosine diphosphate (ADP)
- Adenosine triphosphate (ATP)
Corresponding molecules are formed when the phosphate residues are bound to deoxyadenosine (dAMP; dADP; dATP).
Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) plays a special role in the cell's energy metabolism . The reaction ATP → ADP + P releases energy ; the reaction ADP + P → ATP stores energy chemically.
Cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP) is a very common second messenger for cellular signal transduction .
Adenine is also part of the nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide NAD + , which serves as a coenzyme for hydrogen transfer and thus participates in redox reactions in the cell . Adenine is used for the biosynthesis of the coenzyme S-adenosyl-methionine , which is used in biological methylations , e.g. B. by a Dam methylase .
Part of DNA and RNA
Adenine forms two hydrogen bonds with thymidine in the DNA double helix . During transcription, however, the adenine of the codogenic strand of DNA pairs with the uridine of the mRNA that has just been formed . There are also pairings with dihydrouridine or pseudouridine in the tRNA .

|

|

|

|
| AT base pair (DNA) | AU base pair (RNA) | AD base pair (RNA) | A Ψ base pair (RNA) |
Related links
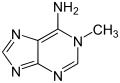
|

|

|

|

|

|
| 1-methyladenine | 2-methyladenine | N 6 -methyladenine | N 6 , N 6 -dimethyladenine | N 6 isopentenyladenine | 2-aminopurine (isoadenine) |
Web links
- Entry for adenines in the Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) , accessed November 19, 2013.
Individual evidence
- ↑ entry to ADENINE in CosIng database of the European Commission, accessed on 27 March 2020th
- ↑ Adenine data sheet (PDF) from Carl Roth , accessed on December 14, 2010.
- ↑ a b entry on adenine. In: Römpp Online . Georg Thieme Verlag, accessed on November 12, 2014.
- ↑ a b c Entry on adenine in the GESTIS substance database of the IFA , accessed on January 8, 2020(JavaScript required) .
- ↑ Adenine data sheet from Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on October 16, 2016 ( PDF ).
- ^ Albert Gossauer, Structure and Reactivity of Biomolecules: An Introduction to Organic Chemistry, Verlag Helvetica Chimica Acta, 2006 .
- ↑ Kossel, A .: About a new base from the animal body. Lecture in: Reports of the German Chemical Society , Issue 18, 1885, p. 79.
- ^ Kossel, A .: Further contributions to the chemistry of the cell nucleus. In: Zeitschrift für Physiologische Chemie , Volume 10, 1886, p. 248.
- ↑ Kossel, A .: About the chemical composition of the cell. Lecture in: Archives for Anatomy and Physiology. Physiological Department , 1891, p. 178.


