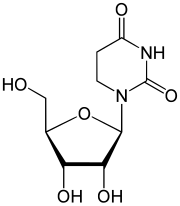
Dihydrouridine
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Dihydrouridine | |||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
|||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 9 H 14 N 2 O 6 | |||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 246.22 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
|||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||||||||
Dihydrouridine (D, UH 2 , Uh) is a nucleoside and occurs in tRNA , rRNA , snRNA and chromosomal RNA . It consists of β- D ribofuranose (sugar) and the nucleobase dihydrouracil . It is created by adding two hydrogen atoms to form uridine , so that a completely saturated ring is created without further double bonds.
properties
Dihydrouridine forms a base pair with adenosine .
Due to the lack of a double bond, the ring is not planar and therefore more flexible. Dihydrouridine considerably destabilizes the C3'- endo conformation of sugar, which is necessary for the formation of the A-type helical RNA. Dihydrouridine, on the other hand, favors the C2'- endo conformation of sugar, which is more flexible than the C3'- endo conformation. Greater conformational flexibility and dynamic motion are found in regions of RNA where tertiary interactions and looping are required simultaneously. While pseudouridine and 2'-O-methylations stabilize the local RNA structure, this is the opposite with dihydrouridine.
Dihydrouridine is represented quite frequently in the tRNA; due to its frequent occurrence in one section, part of the tRNA is referred to as the dihydrouracil arm / loop.
tRNA from organisms that grow at low temperatures ( psychrophiles ) have high 5,6-dihydrouridine contents (40–70% more than the average), which ensure the necessary local flexibility of the tRNA at or below freezing point.
Individual evidence
- ↑ There is not yet a harmonized classification for this substance . A labeling of 5,6-dihydrouridine in the Classification and Labeling Inventory of the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA), accessed on November 5, 2019, is reproduced from a self-classification by the distributor .
- ↑ Patrick A. Limbach, Pamela F. Crain, James A. McCloskey: "Summary: the modified nucleosides of RNA", Nucleic Acids Research , 1994 , 22 (12), pp. 2183-2196 ( doi : 10.1093 / nar / 22.12 .2183 , PMC 523672 (free full text), PMID 7518580 ).
- ↑ JJ Dalluge, T. Hashizume, AE Sopchik, JA McCloskey, DR Davis: "Conformational Flexibility in RNA: The Role of Dihydrouridine", Nucleic Acids Research , 1996 , 24 (6), pp. 1073-1079 ( doi : 10.1093 / nar / 6/24/1073 ; PMC 145759 (free full text); PMID 8604341 ).
- ↑ H. Shi, PB Moore : "The crystal structure of yeast phenylalanine tRNA at 1.93 Å resolution: a classic structure revisited", RNA , 2000 , 6 (8), pp. 1091-1105 ( PMC 1369984 (free full text); PMID 10943889 ).
- ↑ JJ Dalluge, T. Hamamoto, K. Horikoshi, RY Morita, KO Stetter, JA McCloskey: "Posttranscriptional modification of tRNA in psychrophilic bacteria", J. Bacteriol. , 1997 , 179 (6), pp. 1918-1923 ( PMC 178914 (free full text); PMID 9068636 ).
Web links
- Entry for dihydrouridines in the Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) , accessed September 24, 2013.
- Modification Summary of Dihydrouridine in the Modomics database, accessed January 14, 2014.



