Dihydrouracil
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|

|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Dihydrouracil | |||||||||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 4 H 6 N 2 O 2 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 114.10 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
279-281 ° C |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||||||||||||||
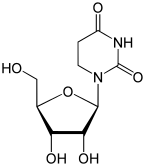
Dihydrouracil is a heterocyclic organic compound with a hydrogenated pyrimidine backbone and two carbonyl groups in positions 2 and 4. The nucleoside of Dihydrouracil is dihydrouridine (D, UH 2 , Uh) occurs in the t RNA . Like uracil, it forms a base pair with adenine .
Emergence
Uracil is hydrogenated in nucleosides by the dihydropyrimidine dehydrogenase to dihydrouracil.
properties
Dihydrouracil is a solid, with a melting temperature of 279-281 ° C.
It forms the base pairing to adenine with two hydrogen bonds in the RNA via the 4-oxo group and the N – H group .
It gives its name to the dihydrouracil loop in the tRNA.
See also
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d data sheet dihydrouracil from Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on November 22, 2013 ( PDF ).
- ↑ H. Shi, PB Moore : "The crystal structure of yeast phenylalanine tRNA at 1.93 Å resolution: a classic structure revisited", in: RNA , 2000 , 6 (8), pp. 1091–1105 ( PMC 1369984 (free full text) ; PMID 10943889 ).
Web links
Wikibooks: Biochemistry and Pathobiochemistry: Pyrimidine Metabolism - Learning and Teaching Materials
Commons : Dihydrouracil - Collection of images, videos and audio files
- Entry for Dihydrouracil in the Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) , accessed November 8, 2013.