3-chlorosalicylic acid
| Structural formula | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|

|
|||||||||||||||||||
| General | |||||||||||||||||||
| Surname | 3-chlorosalicylic acid | ||||||||||||||||||
| other names |
3-chloro-2-hydroxybenzoic acid |
||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 7 H 5 ClO 3 | ||||||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| properties | |||||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 172.57 g mol −1 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
184-186 ° C |
||||||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | |||||||||||||||||||
3-chlorosalicylic acid is a chemical compound that belongs to both the phenol group and the aromatic carboxylic acid group.
presentation
3-chlorosalicylic acid cannot be obtained directly from salicylic acid because the preferred direction of substitution is the 5-position. Therefore, a sulfonic acid group is introduced first, then the chlorination is carried out and finally desulfonation is carried out.
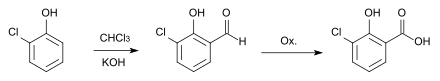
Furthermore, the synthesis via a Reimer-Tiemann reaction and subsequent oxidation of the aldehyde formed with silver oxide is possible.
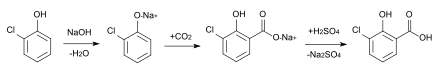
A Kolbe-Schmitt reaction with 2-chlorophenol also gives 3-chlorosalicylic acid, but in a low yield.
Reactions
Oxidation with potassium persulfate turns 3-chlorosalicylic acid into 3-chlorogentisic acid (melting point 220–223 ° C).
proof
The reaction with iron (III) chloride gives an intense purple color.
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c Data sheet 3-Chlorosalicylic acid from Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on March 18, 2011 ( PDF ).
- ↑ NW Hirwe, KN Rana, KD Gavankar: Derivatives of salicylic acid. In: Proceedings of the Indian Academy of Sciences - Section A. 8, 1938, pp. 208-213, doi : 10.1007 / BF03045504 .
- ↑ a b R.L.Crawford, SWHutton, PJChapman: "Purification and Properties of gentisates 1,2-dioxygenase from Moraxella osloensis", in: J. Bacteriol. , 1975 , 121 (3), pp. 794-799; PMC 246005 (free full text).
- ^ A b N. Walker, GH Wiltshire: The decomposition of 1-chloro- and 1-bromonaphthalene by soil bacteria. In: Journal of General Microbiology. 12 (3), 1955, pp. 478-483, doi : 10.1099 / 00221287-12-3-478 , PMID 14392303 .