Serial digital interface
The Serial / Standard Digital Interface ( SDI ) is a serial, digital interface , primarily for the transmission of uncompressed and unencrypted video data via coaxial cables or fiber optic cables . It is mainly used in the field of professional television studios / broadcasters.
The SDI interface is specified by the Society of Motion Picture and Television Engineers (SMPTE) and represents a further development of the analog video standards such as the PAL or NTSC process. Media content is transmitted directly and without interruption. Accordingly, there is no need to search for a source, as the signal is output raw. The term SDI is often used when referring to the connector used for it, but this is a so-called BNC connector. The plug connection is always the same, regardless of whether it is 1.5G, 3G, 6G or 12G, as these relate to the data rate and the cross-section of the cable and not, as is widespread, to the voltage level. SDI cables are an established standard in the TV and film world. The signal is transmitted loss-free up to a length of 100 meters.
The extension HD-SDI according to the SMPTE 292M standard is the currently predominant connection for the transmission of uncompressed image signals for HD , digital intermediate and digital cinema in the studio and production environment. Image, sound and metadata can be transmitted over all HD-SDI connections . HD-SDI, like SDI in general, can be found primarily in professional video equipment; lower-performance interfaces have become established for consumers. HD-SDI devices are usually only found in private or rental studios and cinemas. The interface is also used in event technology, mainly to be able to transmit video signals over longer distances.
A relatively new field of application is the use in video surveillance systems , where this standard can be used to transmit images from special HD cameras over existing coaxial cable installations. In this way, HD-SDI enables high-resolution images in this sector without a complete conversion to IP video. Other applications are field monitors such as those from Atomos or SmalHD. Sound transmission (high-class mixing consoles), image mixer and metadata transmission.
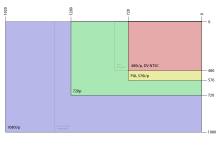
Bit rates and picture formats
The SDI interface is divided into different groups with different bit rates:
- There is the SD-SDI group, which, among other things, map the standard resolutions of PAL or NTSC and is mostly operated at 270 Mbit / s.
- The SMPTE 292M standard describes the HD-SDI interface, which has been used in the context of HDTV formats since 1998 and usually has a bit rate of 1.485 Gbit / s.
- If two HD-SDI connections are interconnected via two cables in accordance with the SMPTE 372M standard, 2K data from digital cinema cameras can also be transmitted.
- An extension of HD-SDI, 3G-SDI , is the activation of two SMPTE-292M connections on just one cable, is operated at 2.97 Gbit / s and is specified in the SMPTE 424M standard.
The most important SDI interface standards are summarized below. The number under video format indicates the number of lines, the subsequent letter i stands for interlaced , as is usual with PAL or NTSC, and p for progressive , image material which is transmitted without interlacing .
| default | Surname | Bit rates (in Gbit / s) | Exemplary video formats |
|---|---|---|---|
| SMPTE 259M | SD-SDI | 0.27, 0.36, 0.143 and 0.177 | 480i (NTSC), 576i ( PAL ) |
| SMPTE 344M | ED-SDI | 0.540 | 480p, 576p |
| SMPTE 292M | HD-SDI | 1.485 and 1.485 / 1.001 | 720p , 1080i (HDTV) |
| SMPTE 372M | Dual Link HD-SDI | 2.970 and 2.970 / 1.001 | 1080p |
| SMPTE 424M | 3G-SDI | 2.970 and 2.970 / 1.001 | 1080p , 4K (Dual Link) |
| SMPTE ST 2081 | 6G UHD-SDI | 6th | 4K |
| SMPTE ST 2082 | 12G UHD-SDI | 12 | 4K |
Physical interfaces

The SDI interface is electrically based on coaxial cable with an impedance of 75 Ω and uses BNC connectors for connection . The cables and connector types used have been adopted from the previous analog video signal standard. The maximum cable length for SD-SDI and the use of high-quality cables is up to 300 m, for HD-SDI the maximum cable length is 100 m. The voltage swing is 800 mV (± 10%).
Furthermore, especially with HD-SDI, optical transmission by means of optical waveguides can also be used. The parameters are specified in the SMPTE 292M, which, among other things, specifies an optical wavelength of 1310 nm (± 40 nm), SC connector and fiber optic cable according to the IEC 60793-2 standard.
The data is independent of the media as NRZI encoded data stream to the receiver, the clock recovery to allow the pixel clock. In addition, the data are made statistically free of DC components by means of a scrambler , so that the SDI data stream can be routed to galvanic isolation via pulse transformers .
Data format
The basic frame structure of an uncompressed digital video signal is described in the SMPTE 259M, which is equivalent to the ITU-R BT.656. The format and the timing are based on the analog video standards. Certain analog specifics, such as the control impulses necessary for horizontal and vertical synchronization, are represented by special digital codes, the SAV ( Start of Active Video ) and EAV ( End of Active Video ).
In SD-SDI, the word length of the transmitted brightness data (Y) and the color information (C b stands for the blue color information or C r for the red color information) is typically 10 bits. In HD-SDI, the Y and C b / C r data are mapped parallel to 10 bits each in a 20-bit wide word.
With SD-SDI, the image information has the following chronological sequence:
Cb Y Cr Y' Cb Y Cr Y'
and with HD-SDI, whereby a Y- and a C-value are always combined in parallel:
- Y
Y Y' Y Y' Y Y' Y Y'- C.
Cb Cr Cb Cr Cb Cr Cb Cr
The image information is transmitted in the YCbCr color model with a scanning raster of 4: 2: 2 and may only cover the value range 4 to 1019 (0x004 to 0x3FB in hexadecimal notation). The values 0 to 3 and 1020 to 1023 (0x3FC to 0x3FF) are reserved for signaling and control words within the framework of the SDI interface. Among other things, these control words are used to signal the start or end of a video line.
Color models
Single Link HD-SDI SMPTE 292M provides
- YCbCr 4: 2: 2 with 10 bits per channel.
Dual Link HD-SDI SMPTE 372M also offers
- higher frame rates for the 1080p formats: 50, 60 / 1.001 and 60
- YCbCr 4: 4: 4 and RGB 4: 4: 4 with 10 bits per channel, with optional alpha channel
- YCbCr 4: 4: 4 and RGB 4: 4: 4 with 12 bits per channel without alpha channel
- YCbCr 4: 2: 2 with 12 bits per channel, with optional alpha channel
Extensions
In addition to the uncompressed video signal, which is primarily transmitted, SDI offers the option of transmitting additional signals, control data or metadata / control data. For this purpose, the time ranges outside the visible video range, which are used for synchronization pulses in the underlying analog video standards, are used to transmit special data packets.
The SMPTE 291M standard specifies how this additional data, referred to in English as ancillary data , can be inserted into the SDI signal. Devices that carry out this insertion or embedding are also referred to as embedders or the counterpart to this as deembedders . For example, the following data can be inserted in addition to the video data:
- EDH packages for error detection ( English Error Detection and Handling ) according to the SMPTE RP168 standard.
- Digital audio data according to the AES-3 standard . Up to 16 uncompressed audio channels can be inserted in both SD-SDI and HD-SDI, the methods of which are specified in SMPTE 272M and SMPTE 299M.
- Timecode for timing.
- Teletext according to the standards SMPTE 2031 or OP-47.
- Text information
- VPID (Video Payload Identifier) to describe the video format (defined in SMPTE 352M).
The advantage of the embedded additional data is that in the infrastructure of a television studio there is no need for separate paths for video signals and the associated audio signals and control signals, as is the case with analog transmission. The image signal contains up to 16 associated audio streams, appropriately correctly timed, and can be routed as a signal sequence with a constant delay time, for example via crossbars .
SDTI
In addition to the transport of uncompressed video data, the SDI interface can use the normally visible area of the video data for the transport of any data. For example, Ethernet interface data or digitally compressed video data according to MPEG or H.264 can be transmitted via existing SDI infrastructure. The procedure is specified in the SDTI ( Serial Data Transport Interface ) so that there are no disruptions in image reproduction . For SD-SDI, SMPTE 305M specifies the details, for HD-SDI the specification SMPTE 348M.
3D
The Digital Cinema Initiatives uses HD-SDI transmission to display 3D content in the cinema with 48P.
literature
- Charles Poynton: Digital Video and HDTV Algorithms and Interfaces . Morgan Kaufmann Publishers, San Francisco 2003, ISBN 1-55860-792-7 .
Norms
- Society of Motion Picture and Television Engineers: SMPTE 292M-2008: 1.5 Gb / s Signal / Data Serial Interface
- Society of Motion Picture and Television Engineers: SMPTE 291M-2006: Ancillary Data Packet and Space Formatting
- Society of Motion Picture and Television Engineers: SMPTE 372M-2009: Dual Link 1.5 Gb / s Digital Interface for 1920 × 1080 and 2048 × 1080 Picture Formats
- Society of Motion Picture and Television Engineers: SMPTE 424M-2006: 3 GB / s Signal / Data Serial Interface
- Society of Motion Picture and Television Engineers: SMPTE 425M-2008: 3 GB / s Signal / Data Serial Interface - Source Image Format Mapping
- Society of Motion Picture and Television Engineers: SMPTE 428M-1-2006: D-Cinema Distribution Master - Image Characteristics
- Society of Motion Picture and Television Engineers: SMPTE 428M-9-2008: D-Cinema Distribution Master - Image Pixel Structure Level 3 - Serial Digital Interface Signal Formatting