8: 2 fluorotelomer alcohol
| Structural formula | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
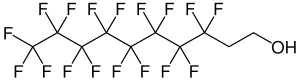
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| General | |||||||||||||||||||
| Surname | 8: 2 fluorotelomer alcohol | ||||||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 10 H 5 F 17 O | ||||||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
white solid |
||||||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| properties | |||||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 464.12 g mol −1 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
48-50 ° C |
||||||||||||||||||
| boiling point |
112–114 ° C (13 hPa) |
||||||||||||||||||
| Vapor pressure |
3 Pa (21 ° C) |
||||||||||||||||||
| solubility |
137 μg l −1 (25 ° C) |
||||||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | |||||||||||||||||||
8: 2-fluorotelomer alcohol ( 8: 2-FTOH ) is a chemical compound that belongs to the group of fluorotelomer alcohols within the per- and polyfluorinated alkyl compounds (PFAS).
Extraction and presentation
8: 2-FTOH is produced by means of telomerization , from which the name is derived.
use
Various consumer products such as textiles or food packaging are finished with perfluorinated surfactants in order to give them water and grease repellent properties. 8: 2 FTOH can be found as an impurity in end products such as paper or cardboard for food packaging.
Biological importance
The product impurities can migrate out of the materials. 8: 2-FTOH can break down to perfluorooctanoic acid ( PFOA ), which is persistent in the environment .
Individual evidence
- ↑ Data sheet 1H, 1H, 2H, 2H-Perfluoro-1-decanol, 97% from Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on December 26, 2019 ( PDF ).
- ↑ a b c M. A. Kaiser, DP Cobranchi, CPC Kao, PJ Krusic, AA Marchione, RC Buck (2004): Physicochemical properties of 8-2 fluorinated Telomer B alcohol . Journal of Chemical and Engineering Data 49 (4): 912-916.
- ↑ a b c data sheet 1H, 1H, 2H, 2H-Perfluoro-1-decanol, 97% from AlfaAesar, accessed on December 26, 2019 ( PDF )(JavaScript required) .
- ↑ Federal Institute for Risk Assessment : Perfluorochemicals in papers and cardboard boxes for food packaging (PDF; 52 kB) . October 2005
- ↑ T. H Begley, K. White, P. Honigfort, ML Twaroski, R. Neches, RA Walker (2005): Perfluorochemicals: Potential sources of and migration from food packaging . Food Additives and Contaminants 22 (10): 1023-1031; doi : 10.1080 / 02652030500183474 .
- ↑ Urs Berger, Dorte Herzke (2006): Per- and Polyfluorinated Alkyl Substances (PFAS) extracted from textile samples ( Memento from December 7, 2015 in the Internet Archive ) (PDF; 99 kB) . Organohalogen Compounds.
- ↑ MJA Dinglasan, Y. Ye, EA Edwards, SA Mabury (2004): Fluorotelomer alcohol biodegradation yields poly- and perfluorinated acids . Environmental Science & Technology 38 (10): 2857-2864; doi : 10.1021 / es0350177 .
Web links
- Fluorotelomere - an undetected risk? (PDF file; 59 kB)