Admiral Makarow (ship, 1906)
|
|
|
|---|---|
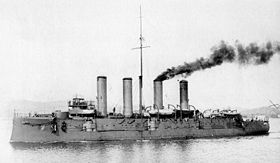 Admiral Makarov |
|
| Overview | |
| Type | Armored cruiser |
| Shipyard | |
| Keel laying | March 22, 1905 |
| Launch | April 26, 1906 |
| delivery | March 29, 1908 |
| Namesake | Stepan Osipovich Makarov |
| period of service |
1906–1918 Russian Navy |
| home port | Kronstadt |
| Whereabouts | Canceled in Szczecin in 1922 |
| Technical specifications | |
| displacement |
7,835 ts ; Max. 8,343 ts |
| length |
137.0 m above sea level, |
| width |
17.5 m |
| Draft |
6.7 m |
| crew |
570 men |
| drive |
26 Belleville boiler |
| speed |
22.5 kn |
| Range |
2,100 nm at 12 kn |
| Armament |
• 2 × 203 mm L / 45 guns in single turrets |
| Bunker quantity |
1,020 tons of coal |
| Armor |
|
| Sister ships | |
The Admiral Makarow was a bayan- class armored cruiser of the Imperial Russian Navy . It was named after Admiral Stepan Ossipowitsch Makarov , who died on April 13, 1904 when his flagship Petropavlovsk sank off Port Arthur .
prehistory
After the type ship Bajan was sunk in Port Arthur during the Russo-Japanese War and lifted by the Japanese, the ship's design was only slightly modified. The bayan , built in 1899–1902, was armored with Harvey nickel steel; the replicas built from 1905 onwards were given the more modern Krupp cemented steel, which resulted in a considerably increased resistance with almost identical armor thickness. In April 1905 the order for a new ship was awarded to the French shipyard of the Bajan , which at the same time provided construction drawings for two replicas at Russian shipyards.
The Admiral Makarow initially differed from the Russian replicas Pallada II and Bajan II by a central mast. This was removed before the First World War and replaced by two masts. During the war, she received a third 203 mm gun with a protective shield between the funnels and the rear mast for her defense tasks in the Riga Bay.
Calls
On December 28, 1908, the Admiral Makarow was with a training ship formation under Rear Admiral Wladimir Iwanowitsch Litvinow in Augusta (Sicily) when a very severe earthquake occurred in nearby Messina . She ran with the ships of the line Slawa and Zessarewitsch immediately with maximum speed to Messina. There the earth continued to shake, preventing the ships from dropping anchors, and the Russians put parts of their crews on land to look for people who had been buried. Already on Wednesday, December 30th, the Admiral Makarow entered the port of Naples with 685 injured. She took over medicines and supplies and returned to Messina, only to leave it on January 1st in the evening for another evacuation trip. Little by little, warships from many nations arrived in the disaster area to support the rescue work.
War mission in the Baltic Sea
The Admiral Makarow served in the Baltic fleet during the First World War . The Russian cruisers ran far into the Baltic Sea several times as cover groups for mine layers. After the loss of the sister ship Pallada , they had to be accompanied by destroyer groups to secure submarines. As the flagship of the 1st Cruiser Brigade of Rear Admiral Mikhail Bachirew took Admiral Makarov on July 2, 1915 the so-called Gotland raid with the sister ship Bajan and protected cruisers Bogatyr and Oleg in part, the East Prussian on the way to the coast on a German minelayer bandage on the March back met. In the ensuing artillery duel, the German mine cruiser SMS Albatross was so badly damaged that it had to be put on the burning beach near Ostergarn on the East Gothenburg coast . The small cruiser SMS Augsburg escaped because the Russian units were concentrating on the Albatross . The large cruiser SMS Roon appeared late on the battlefield and attacked the Russian cruisers that were already withdrawing. He scored a hit on the bayan , but it did not cause much damage.
In 1916 Admiral Makarow was one of the parts of the Russian fleet that defended the Riga Bay. Later she was involved in the battle in Moon Sound on October 17, 1917, where she had arrived from Tallinn after the attack by the Germans to reinforce the defense on Irben Strasse .
From January 25th to 27th, 1918 she moved from Reval to Helsingfors and then took part in the ice march of the Baltic Fleet in April 1918 to Kronstadt .
She was decommissioned on September 7, 1918. In July 1921 it served again as headquarters for the naval headquarters in Petrograd.
Final fate
On August 15, 1922, the Admiral Makarov was sold to the German-Soviet company “Derumetall”, towed to Germany in autumn and broken up there. She was officially removed from the list of the Soviet Navy on November 21, 1925 .
Sister ships
- Bajan (I): Keel laid in February 1899 at Forges & Chantiers, La Seyne, France; June 12, 1900, in service August 1902, sunk in Port Arthur on December 8, 1904; raised by the Japanese and commissioned as Aso ; Sunk as a target ship in 1932.
- Pallada : Keel laid in August 1905 at New Admiralty Shipyard St. Petersburg; Launched on November 10, 1906; in service on February 21, 1911; sunk in the Baltic Seaon October 11, 1914 by German submarine U 26 .
- Bayan (II): Keel laid on August 22, 1905 at the New Admiralty Shipyard St. Petersburg; Launched on August 2, 1907; in service November 30, 1911; broken up in 1922 in Szczecin.
literature
- Conway's Maritime Press: All the World's Fighting Ships 1860-1905. London 1979.
- Johann Ulrich Schlegel: When the end of the world seemed near. In: The earthquake of Messina of 1908. civitas 1/2 2009, p. 12ff.
Web links
- Bajan replicas on infoart in Russian ( Memento from June 24, 2012 in the Internet Archive )
- Side view of Admiral Makarov , 1917 ( Memento from March 5, 2007 in the Internet Archive )

