Ahmadnagar (Sultanate)
| Ahmadnagar | |||||
| 1490-1633 | |||||
|
|
|||||
| Official language | Persian | ||||
| Capital |
Ahmadnagar Parenda Junnar |
||||
| Form of government | sultanate | ||||
| currency | Falus | ||||
| founding | May 28, 1490 | ||||
| resolution | 1633 | ||||
| State religion: Islam Dynasty: Nizam Shahi |
|||||
| Location of Ahmadnagar | |||||
| Tomb of Salabat Khan II | |||||
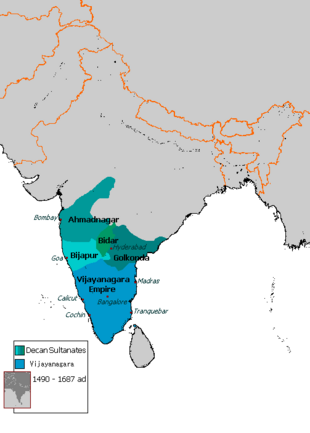
The Sultanate of Ahmadnagar (also Ahmednagar ) was one of the five central Indian Deccan sultanates that emerged from the Bahmani Sultanate . It was founded in 1490 and lasted until it was subjugated by the Mughal Empire in 1633 . The capital was initially Ahmadnagar , later Parenda and Junnar .
history
Ahmad Nizam Shah , a governor of the Bahmani Sultan Mahmud Shah IV , defeated his army in 1490 and proclaimed himself sultan. On the remains of the old city of Bhingar, he founded a new capital, which he named Ahmadnagar after himself. His empire comprised roughly the west and the center of today's Indian state of Maharashtra . The dynasty founded by Ahmad, the Nizam Shahi , initially competed with the Adil Shahi of the neighboring Sultanate of Bijapur , which also emerged from the Bahmanid Empire, for supremacy on the Deccan . In addition, they maintained close relationships with Golkonda . From 1543 to 1553, Ahmadnagar was also allied with the southern Indian Hindu Empire Vijayanagar . In 1558 and 1561 it suffered defeats against Bijapur, but in 1565 it stood on the side of the old enemy as well as Golkondas and Bidars in the Battle of Talikota , in which Vijayanagar was devastated and thus eliminated as a power factor in the Deccan. In 1572 troops invaded the eastern neighboring sultanate of Berar , which was finally annexed in 1574.
Towards the end of the 16th century, the north Indian Mughals, intent on expansion, developed into Ahmadnagar's main competitors. In 1595 they besieged the capital without success. To appease the Mughals, Ahmadnagar resigned Berar in 1596. However, a second invasion soon followed. Despite bitter resistance from the regent Chand Bibi, the Mughals pushed forward and took the capital in 1600. The Nizam Shahi fled to the southeastern fortress Paranda. A few years later, the general Malik Ambar , who came from Abyssinia and was in the service of the Sultan, rose to become the real ruler. With the help of highly mobile Marathic riders who attacked the slower Mughal armies and then withdrew in a flash, he was able to rebuild the empire between 1609 and 1612. In the alliance with Bijapur and Golkonda (since 1615) he invaded the Mughal provinces of Khandesh and Berar from 1616 to 1621 , but after the alliance was broken, a large part of the conquered territories was lost again. Parts of Berar were under the rule of Ahmadnagar until Malik Ambar's death in 1626. The rule of the Nizam Shahi sultans ended in 1633 with the final military defeat against the Mughals and the incorporation of Ahmadnagar into their empire.
literature
- Joseph E. Schwartzberg (Ed.): A historical atlas of South Asia (= The Association for Asian Studies. Reference series. Vol. 2). 2nd impression, with additional material. Oxford University Press, New York NY u. a. 1992, ISBN 0-19-506869-6 .