Bükker culture
|
||||
| expansion | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| northern Hungary, Slovak mountainous country | ||||
| Leitforms | ||||
|
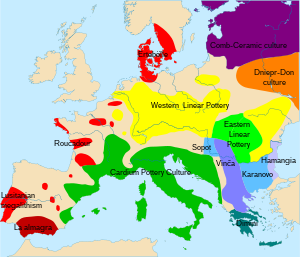
The Bükk culture (also: Bükk culture) is a Neolithic culture of eastern Slovakia and Hungary on the upper reaches and north of the Tisza , especially in the eponymous Bükk Mountains in northern Hungary. There are close relationships with Alföld linear ceramics , the Bükker culture is often seen as its late development.
Typical vessel inventory
Typical is a thin-walled ceramic decorated with parallel ribbon or spiral motifs. The vessels are richly decorated and are characterized by their high ceramic quality. There are mainly kamps , bottle-shaped vessels with a pouring tube and thin-walled bowls. Rich decorations with patterns in arch, garland, ribbon and spiral form are typical. There are also colored incrustations . The Pișcolt culture in north-western Romania has very similar ornament patterns and vessel types, but the former are mostly painted on, not carved.
trade
In neighboring cultures, obsidians from the Zemplen and Tokaj area can be found in this culture . Spondylus mussels from the Mediterranean or Black Sea can be found in the range of the culture .
Settlements
Settlements can be found in the eponymous Bükker Mountains, as well as in the Hungarian lowlands . In addition to pit houses , there were also tell-like settlements with several cultural layers and used caves.
Subsequent culture
The Tisza culture developed along with southern influences in the area of distribution . It incorporated elements of the Bükker culture, the Alföld linear ceramics and the Esztár and Szákálhat cultures.
literature
- Jan Lichardus : Studies on Bükker culture (= Saarbrücker contributions to antiquity. Vol. 12). Dr. Rudolf Habelt GmbH, Bonn 1974, ISBN 3-7749-1306-4 .
- Ferenc of Tompa : A szalagdiszes agyagmuevesség kultúrája magyarországon. A buekki és a tiszai culture. = The band ceramics in Hungary. The Bükker and Theiss cultures (= Archaeologia Hungarica. Vol. 5/6, ISSN 0066-5916 ). sn, Budapest 1929.
Individual evidence
- ^ Mihael Budja: The transition to farming in Southwest Europe: perspectives from pottery. Documenta Praehistorica XXVIII, pp. 27–47 ( Memento of the original from March 4, 2016 in the Internet Archive ) Info: The archive link was inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice.