Bükk
| Bükk | |
|---|---|
|
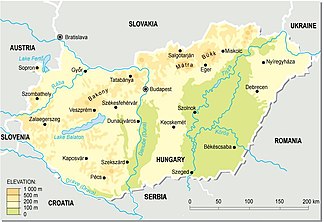
Location of the Bükk in northern Hungary between Eger and Miskolc |
|
|
Lillafüred from the Szeleta summit |
|
| Highest peak | Szilvási-kő (960.7 m) |
| location | Heves / Borsod-Abaúj-Zemplén counties border , Hungary |
| part of | Northern Hungarian Central Mountains |
| Coordinates | 48 ° 2 ′ N , 20 ° 30 ′ E |
| Type | Karst Mountains |
The Bükk is part of the Northern Hungarian Central Uplands . It is the highest karst mountain range in the country. The name Bükk is derived from the Hungarian word for beech , the predominant tree species there. The Bükk is Hungary 's largest contiguous forest area and covers approximately 100,000 hectares . For a long time the highest peak was the Istállós-kő with 959 m. Measurements at the beginning of 2014 showed that the Szilvási-kő is higher: 960.715 meters. Other peaks are the Bálvány with 956 m and the 949 m high Tar-kő . There are about 20 other peaks over 900 m high. The middle area of the low mountain range has had the status of a national park since 1977 .
geology
The bedrock was raised between the Upper Carboniferous and the Middle Jurassic from the North African part of the Tethys . The deposits from a period of 160 million years form the basis for today's rock layers made of limestone , dolomite , sandstone and slate formed from clay . In the Triassic , rhyolite , andesite and basalt were deposited as a result of volcanic eruptions . During the Jura came gabbro added. At the end of this geological age , the Tethys Sea closed. Between the Upper Jurassic and the Eocene , the folded structure was formed when pieces of the oceanic plate crust pushed over the rejuvenated continental plate . In the paleogene the mountains finally rose. At the beginning of the Eocene, the sea advanced again and left traces in the form of sediments. At the end of the Oligocene , layers of rock that were formed 20-25 million years earlier during the Paleocene moved over it . At the beginning of the Miocene , volcanic activity intensified and the area was covered with volcanic rock. Sediments from Lake Pannon can be found in the southern part of the Bükk .
Water reservoir
A special landscape feature is the Bükk plateau, an almost flat area naturally delimited by steep rock faces and slopes, which is only accessible in a few places. The drinking water for half a million people in the area is fed by the waterways on the plateau . These waterways formed the heights of the limestone plateau through river erosion . The rainwater penetrates the cave and crevice system, makes its way through a complex system of rivulets and watercourses and finally emerges at the springs at the foot of the mountains. Some of these springs are only active in spring and are then a popular hiking destination (Vörös-kő-völgyi-időszakos-forrás, Imó-if).
The water is pure and can be passed on to the consumer without additional clarification. On the south side, the drinking water has a particularly pure taste, as it covers a 20–30 km long underground path. In reality, this route is many times longer because the filter system is widely branched. However, it is a sign that cannot be ignored that in June 2006 the drinking water in Miskolc was temporarily polluted as a result of illegal animal husbandry and fertilization .
Caves in the Bükk
There are currently 1072 known caves , many of which can be visited without special training. These include the deepest cave in the country, the 254 m long István Cave, the Anna Cave, the Szeleta Cave, the Kecske Hole and the Istállós-kő Cave . The last three were already used by prehistoric men. The Istállós-kö contained stone and bone implements from the Aurignacia . The lower layer contained about 50 spear points with a split base ( Aurignac points ), the upper one with a solid base ( Lautscher points ). The stone-lined fireplace measuring three by four meters contained charcoal and numerous animal bones, 80% of which were those of young cave bears, and around 2000 animals due to the penis bones found. A special feature is a 45,000 year old, 12 cm long bone flute . Since many caves provide habitat for rare animals, 45 of them are under protection.
Places and communities
- North: Parasznya , Tardona , Dédestapolcsány , Mályinka , Nagyvisnyó
- West: Eger , Felsőtárkány , Szarvaskő , Mónosbél , Bélapátfalva , Szilvásvárad
- South: Kisgyőr , Harsány , Bükkaranyos , Mocsolyás , Latorpuszta , Kács , Tibolddaróc , Cserépváralja , Cserépfalu , Bükkzsérc , Noszvaj , Felsőtárkány
- East: Miskolc , Vadna , Sajószentpéter , Sajóbábony
- In the mountains: Bükkszentkereszt , Répáshuta , Bükkszentlászló , Ómassa , Lillafüred , Hollósteto
tourism
The Bükk is considered to be the lungs of the country, whose extensive nature is protected and cared for. The area is particularly suitable for hiking . Particularly popular with hikers from Eger and Miskolc is the bus, which only runs on Sundays and travels across the southern part of the Bükk, and is an ideal starting point for hikes. Only a few parking spaces are designated for motorized vehicles. There are a variety of tourist associations that offer guided walks.
Attractions
- In Miskolctapolca, near the town of Miskolc, there is the Barlangfürdő thermal bath ("cave bath").
- Where the Szinva and Garadna valleys meet is Lillafüred, where the country's largest waterfall can be found.
- In Szalajka -Tal there is a forest museum and a trout farm .
- There are ski slopes in Bánkút .
- In Bélapátfalva that's Monastery Bélapátfalva and monastery ruins to see.
- The Tar-kő , a cliff at an altitude of 949 m, offers a view of the Alföld .
- The Kecske-lyuk ("goat hole") is a spring cave.
- The periodically active springs at Felsőtárkány .
- Another ruined monastery is Szentlélek ("Holy Spirit").
- The Nagy-mező ("Big Field").
- The Szeleta Cave
- The Őskohó
- The Bél-kő
- The Gerenna and Dédes castle ruins near Szilvásvárad
- The gorges -Tal Sebes-víz
-
Narrow gauge railways :
- Lillafüredi Állami Erdei Vasút ("State Forest Railway Lillafüred ")
- Felsőtárkányi Állami Erdei Vasút (" Felsőtárkány State Forest Railway ")
- Szilvásváradi Erdei Vasút ("Forest Railway Szilvásvárad"), see also Szalajka Railway
See also
- National parks in Hungary
- Bükk culture (also: Bükk culture), Neolithic culture of Eastern Slovakia and Hungary on the upper reaches and north of the Tisza, especially in the eponymous Bükk Mountains in northern Hungary
Web links
- Pictures from the Bükk hegység (Bükk Mountains) in Hungary. Retrieved on December 19, 2010 (German, long-distance hiking).
- Bükk-Aggtelek-Zemplén. Fahrradreisen.de, accessed on November 26, 2008 (German, bike tour description).
- Lillafüredi Állami Erdei Vasút in the Hungarian language Wikipedia (Waldbahn Lillafüred: pictures, route map)
Individual evidence
- ↑ The Bükk has a new summit article d. Hungarian web newspaper "Index"