Growth factor BDNF
| Growth factor BDNF | ||
|---|---|---|
|
||
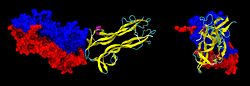
| Surface / ribbon model of the tetramer from two sides, according to PDB 1BND | ||
| Properties of human protein | ||
| Mass / length primary structure | 119 amino acids | |
| Secondary to quaternary structure | Monomer, homodimer | |
| Precursor | (229 aa) | |
| Isoforms | 5 | |
| Identifier | ||
| Gene names | BDNF ANON2; BULN2 | |
| External IDs | ||
| Occurrence | ||
| Parent taxon | Vertebrates | |
| Orthologue | ||
| human | House mouse | |
| Entrez | 627 | 12064 |
| Ensemble | ENSG00000176697 | ENSMUSG00000048482 |
| UniProt | P23560 | P21237 |
| Refseq (mRNA) | NM_001143805 | NM_001048139 |
| Refseq (protein) | NP_001137277 | NP_001041604 |
| Gene locus | Chr 11: 27.65 - 27.72 Mb | Chr 2: 109.67 - 109.73 Mb |
| PubMed search | 627 |
12064
|
The growth factor BDNF (from English: "Brain-derived neurotrophic factor"; dt. Approximately: "Neurotrophic factor originating from the brain") is a protein from the group of neurotrophins and is closely related to the nerve growth factors . It occurs in all vertebrates . Mutations in the human BDNF - gene are a cause for Ondine's curse and are associated with the WAGR syndrome and the risk of bulimia nervosa type second
Function and occurrence
BDNF acts on various neurons in the central and peripheral nervous systems . It helps protect existing neurons and synapses and promotes the growth of new ones. In the brain, it is active in the hippocampus , the cerebral cortex and the forebrain , i.e. in areas that are fundamental to memory and abstract thinking. Here, BDNF also plays a major role in long-term memory. BDNF is one of the most active neurotrophins and is especially important in adult neurogenesis . Animal experiments show that mice without BDNF have developmental deficits in the brain and the sensorium and usually die shortly after birth. BDNF is found not only in the brain, but also in numerous cell types and tissues , the retina , the kidneys , the prostate, and human saliva .
BDNF and diseases
Various studies suggest that a deficiency or excess of BDNF is associated with depression , schizophrenia , obsessive-compulsive disorder , Alzheimer's disease , Huntington 's disease , dementia , anorexia nervosa , bulimia nervosa and Rett syndrome . Even epilepsy and irritable bowel syndrome have been associated with a change in BDNF.
Individual evidence
- ↑ IPR020430 Brain-derived neurotrophic factor. In: InterPro. EBI, accessed November 4, 2010 .
- ↑ Binder DK, Scharfman HE: Brain-derived neurotrophic factor . In: Growth Factors . 22, No. 3, September 2004, pp. 123-31. doi : 10.1080 / 08977190410001723308 . PMID 15518235 . PMC 2504526 (free full text).
- ↑ UniProt P23560
- ↑ Acheson A, Conover JC, Fandl JP, DeChiara TM, Russell M, Thadani A, Squinto SP, Yancopoulos GD, Lindsay RM: A BDNF autocrine loop in adult sensory neurons prevents cell death . In: Nature . 374, No. 6521, March 1995, pp. 450-3. doi : 10.1038 / 374450a0 . PMID 7700353 .
- ↑ Huang EJ, Reichardt LF: Neurotrophins: roles in neuronal development and function . In: Annu. Rev. Neurosci. . 24, 2001, pp. 677-736. doi : 10.1146 / annurev.neuro.24.1.677 . PMID 11520916 . PMC 2758233 (free full text).
- ↑ Yamada K, Nabeshima T: Brain-derived neurotrophic factor / TrkB signaling in memory processes . In: J Pharmacol Sci . 91, No. 4, April 2003, pp. 267-70. doi : 10.1254 / jphs.91.267 . PMID 12719654 .
- ↑ Bekinschtein P, Cammarota M, Katche C, Slipczuk L, Rossato JI, Goldin A, Izquierdo I, Medina JH: BDNF is essential to promote persistence of long-term memory storage . In: Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA . 105, No. 7, February 2008, pp. 2711-6. doi : 10.1073 / pnas.0711863105 . PMID 18263738 . PMC 2268201 (free full text).
- ↑ Ernfors P, Kucera J, Lee KF, Loring J, Jaenisch R: Studies on the physiological role of brain-derived neurotrophic factor and neurotrophin-3 in knockout mice . In: Int. J. Dev. Biol . 39, No. 5, October 1995, pp. 799-807. PMID 8645564 .
- ↑ Mandel AL, Ozdener H, Utermohlen V: Identification of pro- and mature brain-derived neurotrophic factor in human saliva . In: Arch Oral Biol.. . 54, No. 7, July 2009, pp. 689-95. doi : 10.1016 / j.archoralbio.2009.04.005 . PMID 19467646 . PMC 2716651 (free full text).
- ↑ Dwivedi Y: Brain-derived neurotrophic factor: role in depression and suicide . In: Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat . 5, 2009, pp. 433-49. PMID 19721723 . PMC 2732010 (free full text).
- ↑ Brunoni AR, Lopes M, Fregni F: A systematic review and meta-analysis of clinical studies on major depression and BDNF levels: implications for the role of neuroplasticity in depression . In: Int. J. Neuropsychopharmacol. . 11, No. 8, December 2008, pp. 1169-80. doi : 10.1017 / S1461145708009309 . PMID 18752720 .
- ↑ Xiu MH, Hui L, Dang YF, De Hou T, Zhang CX, Zheng YL, Chen DC, Kosten TR, Zhang XY: Decreased serum BDNF levels in chronic institutionalized schizophrenia on long-term treatment with typical and atypical antipsychotics . In: Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry . 33, No. 8, August 2009, pp. 1508-1512. doi : 10.1016 / j.pnpbp.2009.08.011 . PMID 19720106 .
- ↑ Maina G, Rosso G, Zanardini R, Bogetto F, Gennarelli M, Bocchio-Chiavetto L: Serum levels of brain-derived neurotrophic factor in drug-na? Ve obsessive-compulsive patients: A case-control study . In: J Affect Disord . 122, No. 1-2, August 2009, pp. 174-8. doi : 10.1016 / j.jad.2009.07.009 . PMID 19664825 .
- ^ Zuccato C, Cattaneo E: Brain-derived neurotrophic factor in neurodegenerative diseases . In: Nat Rev Neurol . 5, No. 6, June 2009, pp. 311-22. doi : 10.1038 / nrneurol.2009.54 . PMID 19498435 .
- ↑ Zajac MS, Pang TY, Wong N, Weinrich B, Leang LS, Craig JM, Saffery R, Hannan AJ: Wheel running and environmental enrichment differentially modify exon-specific BDNF expression in the hippocampus of wild-type and pre-motor symptomatic male and female Huntington's disease mice . In: Hippocampus . 20, No. 5, June 2009, p. NA. doi : 10.1002 / hipo.20658 . PMID 19499586 .
- ↑ Arancio O, Chao MV: Neurotrophins, synaptic plasticity and dementia . In: Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. . 17, No. 3, June 2007, pp. 325-30. doi : 10.1016 / j.conb.2007.03.013 . PMID 17419049 .
- ↑ Mercader JM, Fernández-Aranda F, Gratacòs M, Ribasés M, Badía A, Villarejo C, Solano R, González JR, Vallejo J, Estivill X: Blood levels of brain-derived neurotrophic factor correlate with several psychopathological symptoms in anorexia nervosa patients . In: Neuropsychobiology . 56, No. 4, 2007, pp. 185-90. doi : 10.1159 / 000120623 . PMID 18337636 .
- ↑ Kaplan AS, Levitan RD, Yilmaz Z, Davis C, Tharmalingam S, Kennedy JL: A DRD4 / BDNF gene-gene interaction associated with maximum BMI in women with bulimia nervosa . In: Int J Eat Disord . 41, No. 1, January 2008, pp. 22-8. doi : 10.1002 / eat.20474 . PMID 17922530 .
- ↑ Zeev BB, Bebbington A, Ho G, Leonard H, de Klerk N, Gak E, Vecsler M, Vecksler M, Christodoulou J: The common BDNF polymorphism may be a modifier of disease severity in Rett syndrome . In: Neurology . 72, No. 14, April 2009, pp. 1242-7. doi : 10.1212 / 01.wnl.0000345664.72220.6a . PMID 19349604 . PMC 2677489 (free full text).
- ↑ Gall C, Lauterborn J, Bundman M, Murray K, Isackson P: Seizures and the regulation of neurotrophic factor and neuropeptide gene expression in brain . In: Epilepsy Res Suppl . 4, 1991, pp. 225-45. PMID 1815605 .
- ↑ Zhang Y, Qin G, Liu Dr, Wang Y, Yao Sk: Increased Expression of Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor Is Correlated With Visceral Hypersensitivity in Patients With Diarrhea-Predominant Irritable Bowel Syndrome. January 14, 2019, accessed on May 24, 2020 .
Web links
- OrphaNet: WAGR syndrome
- Cotman CW, Berchtold NC: BDNF and Alzheimer's Disease — What's the Connection? ( English ) In: Alzforum: Live Discussions . Alzheimer's Research Forum. January 28, 2004. Archived from the original on March 2, 2004. Retrieved on August 21, 2008.
- Patten-Hitt E: Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor (BDNF) ( English ) In: Sciencexpress . The HDLighthouse, Huntingtons Disease: Information and Community. June 14, 2001. Archived from the original on July 15, 2006. Retrieved on August 21, 2008.
- Highfield R: Brain scans 'could reveal mental strength' ( English ) In: Science . Telegraph.co.uk. October 18, 2007. Archived from the original on May 31, 2008. Retrieved August 21, 2008: "Low BDNF activity promotes resilience"