Baptifolin
| Structural formula | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
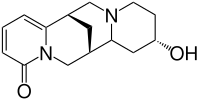
|
|||||||||||||
| General | |||||||||||||
| Surname | Baptifolin | ||||||||||||
| other names |
|
||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 15 H 20 N 2 O 2 | ||||||||||||
| Brief description |
colorless solid |
||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | |||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||
| properties | |||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 260.15 g mol −1 | ||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
||||||||||||
| Melting point |
210 ° C |
||||||||||||
| solubility |
Easily soluble in water and ethanol |
||||||||||||
| safety instructions | |||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | |||||||||||||
Baptifolin is a naturally occurring alkaloid and belongs to the subgroup of quinolizidine alkaloids .
Occurrence
Baptifolin occurs in many plants as a secondary plant substance . For example, in addition to sparteine , anagyrin , cystinine and lupanine , it occurs in the indigolupine ( Baptisia australis , or blue dye pod). The indigolupine occurs predominantly in central and eastern North America, extracts from the root are used medicinally. Baptifolin can also be detected in the roots of Sophora flavescens - a plant from the family of the butterflies - and is found in many coffee products and in Indian cradles ( Caulophyllum thalictroides , blue buttercup). The root of the Indian cradle, which besides Baptifolin also contains methylcytisine , anagyrine and magnoflorine , is known from folk medicine as a means of stimulating labor and relieving spasms.
synthesis
In the first step, the cytisine 1 , which can be synthesized completely, is converted into the N -chlorine compound 2 using sodium hypochlorite . Heterocyclic bond cleavage eliminates chloride of 2 as potassium chloride , and the hydroxide ion of potassium hydroxide also splits off water . The imine 3, which has a polarized C = N double bond, is formed regioselectively .
In the following step, the Grignard compound from allyl bromide is used to create a new CC bond on the allyl cytisine 4 . The Grignard reaction takes place in two steps : first the new CC bond is formed and then MgBrOH is split off under the action of water. The allyl cytisine 4 is then mixed with formaldehyde and, after hydrolysis, the epi -Baptifolin 5 is formed in phosphate buffer solution .
Epi -Baptifolin differs among other things. a. by a slightly higher melting point of 215 ° C of Baptifolin 6 and by the axial position of the hydroxyl group on the C13 atom. Both molecules are in equilibrium with each other and in natural synthesis both occur in parallel in plants.
literature
- Tibebe Z. Woldemariam, Joseph M. Betz, Peter J. Houghton: Analysis of aporphine and quinolizidine alkaloids from Caulophyllum thatictroides by densitometry and HPLC , in: Journal of Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Analysis , 1997 , 15 (6), pp. 839-843 ; doi : 10.1016 / S0731-7085 (96) 01919-X .
- Ferdinand Bohlmann, Dieter Rahtz, Christian Arnd: The alkaloids from Sophora flavescens , in: Chemical reports , 1958 , 91 (10), pp. 2189-2193; doi : 10.1002 / cber.19580911026 .
Individual evidence
- ^ A b J. S. Glasby: Encyclopedia of the Alkaloids (AH) . 1st edition. Plenum Press, New York 1975 , p. 194; ISBN 0-306-30845-2 .
- ↑ Baptifoline (FDB011525). In: foodb.ca. Retrieved July 7, 2017 .
- ↑ This substance has either not yet been classified with regard to its hazardousness or a reliable and citable source has not yet been found.
- ↑ A.-M. Beer, J. Lukanov, P. Sagorchev: The effect of Caulophyllum D4 on the spontaneous contractile activity of the smooth muscles , in: Obstetrics and Frauenheilkunde , 2000 , 60 (9), pp. 456–458; doi : 10.1055 / s-2000-8022 .
- ^ F. Bohlmann , E. Winterfeldt, H. Overwien, H. Pagel: Synthesis of the alkaloids Angustifolin, Baptifolin and Thermopsin , in: Chemischeberichte , 1961 , 95 (4), pp. 944-948; doi : 10.1002 / cber.19620950419 .


