Benzoyl nitrate
| Structural formula | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
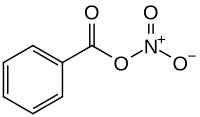
|
|||||||
| General | |||||||
| Surname | Benzoyl nitrate | ||||||
| Molecular formula | C 7 H 5 NO 4 | ||||||
| Brief description |
oily liquid |
||||||
| External identifiers / databases | |||||||
|
|||||||
| properties | |||||||
| Molar mass | 167.12 g mol −1 | ||||||
| Physical state |
liquid |
||||||
| density |
1.521 g cm −3 |
||||||
| solubility |
soluble in acetonitrile, benzene, carbon tetrachloride |
||||||
| safety instructions | |||||||
|
|||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | |||||||
Benzoyl nitrate is an organic compound that can be assigned to the group of organic nitrates . It can also be seen as a mixed anhydride of benzoic acid and nitric acid . In organic synthesis it is used as a reagent for nitration and oxidation reactions.
Extraction and presentation
The compound is synthesized by reacting benzoyl chloride with silver nitrate in acetonitrile at −20 ° C, whereby the solid by-product silver chloride can easily be filtered off. Alternatively, this synthesis can also be carried out in carbon tetrachloride as a solvent.
Because of the thermal instability, the connection is not isolated, but only made in solution.
properties
Benzoyl nitrate solutions are unstable and should be stored at −40 ° C. For the reactivity of the compound, an equilibrium reaction is established with the formation of dinitrogen pentoxide as a reactive species and benzoic anhydride .
Rapid hydrolysis to benzoic acid and nitric acid occurs with water . The thermolysis in boiling carbon tetrachloride yields as products chlorobenzene , benzoic acid, something nitrobenzene and carbon dioxide . In boiling benzene to biphenyl , benzoic acid, benzoic acid and nitrobenzene obtained.
use
Aromatic compounds can be nitrated using benzoyl nitrate . Mixtures of the variously substituted isomers are obtained with toluene or o- xylene . 4,4 '' - Dinitroterphenyl results from p -terphenyl . Secondary amines can be converted into the corresponding nitramines by introducing the nitro group on the amine nitrogen .
The reaction with primary anilines leads to the corresponding N -phenylbenzamides. Thiophenol is oxidized to diphenyl disulfide . At temperatures below 0 ° C the targeted oxidation of thioethers to the corresponding sulfoxides succeeds . When reacted with alcohols , the corresponding aliphatic nitrates can be obtained.
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c A. V. Topchiev: Nitration of Hydrocarbons and other Organic Compounds . Elsevier, 2013, ISBN 978-1-4831-8438-8 , pp. 284 ( limited preview in Google Book search).
- ^ Carl L. Yaws: The Yaws Handbook of Physical Properties for Hydrocarbons and Chemicals Physical Properties for More Than 54,000 Organic and Inorganic Chemical Compounds, Coverage for C1 to C100 Organics and Ac to Zr Inorganics . Gulf Professional Publishing, 2015, ISBN 978-0-12-801146-1 , pp. 141 ( limited preview in Google Book search).
- ↑ a b c d e-EROS Encyclopedia of Reagents for Organic Synthesis , 1999-2013, John Wiley and Sons, Inc., entry for Benzoyl Nitrate, accessed August 8, 2013 .
- ↑ This substance has either not yet been classified with regard to its hazardousness or a reliable and citable source has not yet been found.
- ↑ a b c Francis Francis: About Benzoyl Nitrate, a New Nitriding Agent . In: Reports of the German Chemical Society . 39, No. 4, 1906, pp. 3798-3804, doi : 10.1002 / cber.19060390452 .
- ^ A b c Michael E. Kurz, Lin Tien A. Yang, Edward P. Zahora, Richard C. Adams: Nitration by aroyl nitrates . In: The Journal of Organic Chemistry . 38, No. 13, 1973, pp. 2271-2277, doi : 10.1021 / jo00953a001 .
- ^ A b V. Gold, ED Hughes, CK Ingold: Kinetics and mechanism of aromatic nitration. Part V. Nitration by acyl nitrates, particularly by benzoyl nitrate . In: Journal of the Chemical Society (Resumed) . No. 0, 1950, pp. 2467-2473, doi : 10.1039 / JR9500002467 .
- ↑ I. Horáček, F. Hrabák: Thermal decomposition of acyl nitrates . In: Collection of Czechoslovak Chemical Communications . 39, No. 9, 1974, pp. 2608-2612, doi : 10.1135 / cccc19742608 .
- ^ LR Barlow: The free radical decomposition of benzoyl nitrate and its pressure dependence . In: Tetrahedron . 24, No. 13, 1968, pp. 4913-4915, doi : 10.1016 / S0040-4020 (01) 98688-0 .
- ↑ Michael E. Kurz, S. Eugene. Woodby: Concurrent nitration and oxygenation of o-xylene and hemimellitene with aroyl nitrates . In: The Journal of Organic Chemistry . 41, No. 14, 1976, pp. 2443-2447, doi : 10.1021 / jo00876a019 .
- ↑ a b Thomas Howard Butler: About the implementation of benzoyl nitrate with amines . In: Reports of the German Chemical Society . 39, No. 4, 1906, pp. 3804-3807, doi : 10.1002 / cber.19060390453 .
- ^ Robert Louw, Hans PW Vermeeren, Joost JA van Asten, Willem J. Ultée: Reaction of sulphides with acyl nitrates; a simple and rapid method for preparing sulphoxides . In: Journal of the Chemical Society, Chemical Communications . No. 13, 1976, pp. 496-497, doi : 10.1039 / C39760000496 .


