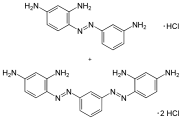
Bismarck brown Y
| Structural formula | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|

|
|||||||||||||||||||
| General | |||||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Bismarck brown Y | ||||||||||||||||||
| other names | |||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 18 H 20 Cl 2 N 8 (dihydrochloride) | ||||||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| properties | |||||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 419.32 g mol −1 | ||||||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | |||||||||||||||||||
Bismarck brown Y or Vesuvin is a dye from the series of cationic azo dyes . The dye was named after Otto von Bismarck , the founder and first chancellor of the German Empire . It was discovered in 1863 by Carl Alexander von Martius as the first bisazo dye.
Manufacturing
Bismarck brown Y is synthesized by diazotization and azo coupling of m -phenylenediamine in a one-pot reaction .
properties
Bismarck brown Y has an absorption maximum at 463 nm in water. It is 1–5% (w / v) soluble in water, 1–3% (w / v) in ethanol and 7% (w / v) in ethylene glycol . His pK s value is the fifth
use
Bismarck brown is used in leather , paper and wood dyeing and for the synthesis of polyazo dyes . It is also used in botany for staining plant cell walls and in microbiology for staining bacteria in a modified Gram stain . Robert Koch was able to detect the tubercle bacilli with Bismarck brown.
Similar dyes
- Bismarck brown R (CI Basic Brown 4) is obtained by an azo coupling using 2,4-diaminotoluene as the diazo and coupling component. It has a redder shade compared to Bismarck brown Y, but otherwise has the same coloring properties. It has also been used on acrylamide gels to optimize the staining of proteins.
- Bismarck brown G is a mixture of dyes which, in addition to Bismarck brown Y, contains a monoazo dye that is created when simply diazotized m-phenylenediamine is coupled onto itself.
Bismarck Brown G; PubChem 24181122
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b Bismarckbraun Y data sheet from Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on March 13, 2011 ( PDF ).
- ↑ W. Müller (Ed.): Handbuch der Farbenchemie. Basics, technology, applications . Ecomed Publishing Company; 3. Supplementary delivery 2003; ISBN 3-609-72700-4 ; P. 2.
- ^ Wilhelm Strube: The historical way of chemistry, Aulis-Verlag, Cologne 1989, p. 276.
- ↑ External identifiers or database links to CI Basic Brown 4 : CAS number: 8005-78-5, EC number: 232-341-8, ECHA InfoCard: 100.029.399 , PubChem : 135516985 , ChemSpider : 26501926 , Wikidata : Q72444823 .
- ↑ W. Müller (Ed.): Handbuch der Farbenchemie. Basics, technology, applications . Ecomed Publishing Company; 3. Supplementary delivery 2003; ISBN 3-609-72700-4 ; P. 24 (Chapter 4.7).
literature
- P. Karrer: Textbook of organic chemistry . 10th edition. Thieme, Stuttgart 1948, p. 514.
- N. Welsch, CC Liebmann: Colors - nature, technology, art . Spectrum, Heidelberg a. Berlin 2003, p. 204.
- Richard W. Horobin, JA Kiernan, and John A. Kiernan: Conn's Biological Stains: A Handbook of Dyes, Stains and Fluorochromes for Use in Biology and Medicine . Garland Pub, 10th edition, 2002; ISBN 1-85996-099-5 ; Pp. 139-140.