Camostat
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
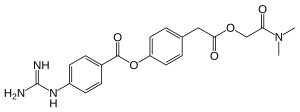
|
||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||
| Non-proprietary name | Camostat (INNv) | |||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
|||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 20 H 22 N 4 O 5 | |||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| Drug information | ||||||||||||||||
| ATC code | ||||||||||||||||
| Drug class |
Protease inhibitors |
|||||||||||||||
| Mechanism of action |
Antifibrinolytic |
|||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 398.41 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||||||||
Camostat is a synthetically produced active ingredient from the group of protease inhibitors . It is approved in Japan as Foipan (manufacturer: Ono Pharmaceutical ) for the oral treatment of chronic inflammation of the pancreas ( pancreatitis ) and postoperative inflammation of the esophagus ( reflux esophagitis ) caused by the reflux of stomach acid .
Chemically, camostat a derivative ( derivative ) of the p -aminobenzoic acid . The active ingredient is used medicinally as camostat mesilate , i.e. the salt of methanesulphonic acid .
Mechanism of action
Camostat inhibits various pancreatic and plasmatic proteolytic enzymes such as trypsin , plasmin , pancreatic kallikrein , plasma kallikrein and thrombin as well as the hydrolytic activity of C1r and C1 esterase in vitro .
Camostat also inhibits the cellular protease TMPRSS2 in vitro . After autocatalytic activation, this enzyme is expressed on the human cell surface, especially in the small intestine and to a lesser extent in the liver, heart, prostate, thymus and lungs.
Therapeutic and experimental use
According to studies, SARS-CoV-2 , the virus responsible for COVID-19 , requires TMPRSS2 , which is present in the human body, in order to penetrate the host cell , which could represent a starting point for treatment. The effectiveness of the drug in cell cultures has already been proven. A therapeutic efficacy in COVID-19 patients has yet to be tested in clinical studies. At the Primate Center in Göttingen it is also planned to investigate whether the active ingredient can be injected directly into the lungs. It is unclear whether Camostat per se is sufficiently available in the lungs. According to Karl Broich , head of the Federal Institute for Drugs and Medical Devices , the necessary dosages, extrapolated from results from the cell cultures, would be so strong in patients with standard weight that serious side effects could occur.
Foipan (Camostat) is one of the drugs for which the Federal Ministry of Health initiated central procurement for the treatment of infected and seriously ill COVID-19 patients in Germany in April 2020. Since Covid-19 therapy is an individual healing attempt without clinical proof of effectiveness, its use should primarily be considered on a patient-by-patient basis in severe forms.
See also
Individual evidence
- ↑ There is not yet a harmonized classification for this substance . A labeling of Camostat Mesylate in the Classification and Labeling Inventory of the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA), which was retrieved on July 15, 2020, is reproduced from a self-classification by the distributor .
- ↑ Product information FOIPAN Tablets 100 mg , Ono Pharmaceutical, as of August 2009 ( PDF ), accessed on March 25, 2020.
- ↑ External identifiers or database links to camostat mesilate : CAS number: 59721-29-8, EC number: 694-565-6, ECHA InfoCard: 100.222.806 , PubChem : 5284360 , ChemSpider : 39251 , Wikidata : Q23731028 . . Molar mass: 494.52 g mol . Sum formula: C 21 H 26 N 4 O 8 S.
- ↑ Camostat mesilate , Japanese Pharmacopoeia (J.P.), p. 204 ( PDF 5 MB)
- ^ S. Fujii, Y. Hitomi: New synthetic inhibitors of C1r, C1 esterase, thrombin, plasmin, kallikrein and trypsin . Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Enzymology, Vol. 661 (1981), pp. 342-345 doi : 10.1016 / 0005-2744 (81) 90023-1
- ↑ LM Reinke: Identification and functional characterization of TMPRSS2 cleavage sites in the spike protein of the SARS coronavirus. Dissertation, Medical Faculty of the Georg-August University in Göttingen, 2016.
- ↑ T. Dingermann: Japanese drug could work against SARS-CoV-2 . Pharmaceutical Newspaper, March 6, 2020.
- ^ A b Anja Martini, Christian Drosten : Coronavirus Update. (PDF) Episode 22. In: ndr.de. Norddeutscher Rundfunk, March 26, 2020, p. 8 , accessed on March 27, 2020 .
- ↑ S. Siebenand: Japanese active ingredient is being tested for Covid-19 in Denmark , Pharmazeutische Zeitung April 1, 2020.
- ↑ Julia Köppe: "Our studies with human lung cells are very promising". In: spiegel.de. March 25, 2020, accessed March 26, 2020 .
- ↑ Veronika Hackenbroch, Kerstin Kullmann: When will Covid-19 be curable? In: Der Spiegel . No. 12 , 2020, p. 46 f . ( online - December 2020 ).
- ↑ Ulla Thiede: Do we have a drug against Covid-19 soon? In: general-anzeiger-bonn.de. April 10, 2020, accessed April 13, 2020 .
- ↑ Information from the institutions and authorities: BMG: Central procurement of pharmaceuticals for the treatment of serious cases of COVID-19 infected patients and distribution to pharmacies by the Bundeswehr , Drugs Commission of German Pharmacists (AMK), news of March 24, 2020.