Casimir Lefaucheux
Casimir Lefaucheux (born January 26, 1802 in Bonnétable , † August 9, 1852 in Paris ) was a French gunsmith and armourer and the inventor of the Lefaucheux cartridge .
Life
Casimir Lefaucheux received his first patent for a breech loader in 1827 . In 1832, he improved his invention by adding a drop barrel to a sporting weapon . The corresponding paper cartridges were reinforced with cardboard in the bottom area and ignited via primers that were common at the time . Weapons of this type were tested by the French army, but rejected because the cartridges were not robust enough.
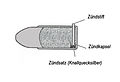
Lefaucheux invented one of the first effective and independent cartridge systems in 1836 , which he equipped with a pen ignition. In doing so, he followed the pioneering work of Jean Samuel Pauly from 1808 to 1812. The Lefaucheux cartridge consisted of a short copper case with the ignition mechanism, black powder and a cardboard case with the projectile or shot package inserted . Lefaucheux also developed one of the first well-functioning breech loading systems.
In 1846, Benjamin Houllier improved the Lefaucheux system by replacing the two-piece sleeve with an all-metal sleeve made of copper or brass . Casimir Lefaucheux took in 1851 at the World Exhibition Great Exhibition in London in part. There he was honored with an award for his cartridges. At the same time he presented a weapon for his cartridge in the form of a bundle revolver at the world exhibition . This bundle revolver was the first practically functioning hand weapon with a single cartridge.
Eugène Lefaucheux
Casimir Lefaucheux's son, Eugène Lefaucheux, continued his father's work and improved the system. As early as 1854 - before Rollin White - he had the cylindrically bored revolver drum patented in France. In 1858 the Lefaucheux M1858 revolver was introduced by the French Navy . It was the first revolver with metal cartridges to be accepted into civil service.
Illustrations
literature
- Gerard Henrotin: Lefaucheux 7mm pinfire revolver explained . HLebooks.com, 2013.
- Gerard Henrotin: European percussion & pinfire shotguns explained . HLebooks.com, 2011.
- Jeff Kinard: Pistols: An Illustrated History of Their Impact (Weapons and Warfare) . Ed .: Spencer C. Tucker . ABC-CLIO , Santa Barbara 2004, ISBN 978-1-85109-470-7 (English).
- Guillaume van Mastrigt: Eugène Lefaucheux ou l'apothéose de la saga familiale . Ed .: Editions Crépin Leblond. 2013 (French).
Individual evidence
- ^ John Walter: Rifles of the World . KP Books, 2006, ISBN 978-0-89689-241-5 , pp. 258 (English).
- ↑ a b c d Jeff Kinard: Pistols. Pp. 109–110 ( Google Books )
- ↑ James H. Willbanks: Machine Guns: An Illustrated History of Their Impact. P. 15 ( Google Books )
- ↑ a b Herbert G. Houze, Carolyn C. Cooper, Elizabeth Mankin Kornhauser: Samuel Colt: Arms, Art, and Invention. Yale University Press , 2006, ISBN 978-0-300-11133-0 , p. 115 ( Google Books )
- ^ Edward Clinton Ezell : Handguns of the World , Stackpole Books, 1981 ISBN 0-88029-618-6 , p. 45
| personal data | |
|---|---|
| SURNAME | Lefaucheux, Casimir |
| BRIEF DESCRIPTION | French gunsmith and armorer |
| DATE OF BIRTH | January 26, 1802 |
| PLACE OF BIRTH | Bonnétable |
| DATE OF DEATH | August 9, 1852 |
| Place of death | Paris |