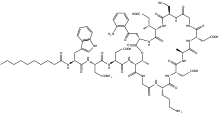
Daptomycin
| Daptomycin | ||
|---|---|---|
|
||
| Rod model according to PDB 1XT7 (NMR) | ||
| Mass / length primary structure | 11 amino acids, 1621 da | |
| Identifier | ||
| External IDs |
|
|
| Drug information | ||
| ATC code | J01 XX09 | |
| DrugBank | BTD00111 | |
| Drug class | antibiotic | |
Daptomycin is an antibiotic and the first representative of the group of cyclic lipopeptides on the market. Daptomycin is currently the most potent bactericidal agent on the market. The drug is mainly used for skin and soft tissue infections with gram-positive problem germs (for example methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus , MRSA for short). At the moment (12/2009) the active ingredient is usually still effective when reserve antibiotics such as linezolid or vancomycin lead to therapy failure due to resistance.
structure
Daptomycin is a cyclic lipopeptide . It consists of an amino acid ring and a decanoyl side chain.
Mechanism of action
Daptomycin has a bactericidal effect. The lipopeptide is built into the cell membrane of gram-positive bacteria in a calcium-dependent manner. This leads to the formation of membrane pores through which mainly potassium ions flow out. This creates a depolarization of the membrane potential . Furthermore, according to experimental findings, the bacterial DNA, RNA and protein synthesis is disturbed, which causes the bactericidal effect of the substance.
It is important and interesting that the pores are built into the membrane only, not into the cell wall . As a result, there is no cell lysis. Daptomycin is thus a bactericidally effective antibiotic without cell lysis.
Scientists from the Universities of Bonn and Amsterdam , the Ruhr University Bochum , the University of Newcastle and the German Center for Infection Research (DZIF) demonstrated in a study in 2016 that daptomycin inhibits the cell wall synthesis of bacteria.
Pharmacokinetics
The agent must be administered intravenously because it is not sufficiently absorbed enterally . The substance can be administered as a 30-minute infusion and as a 2-minute injection. It is available as a powder and should be administered once a day for 7-14 days (for dosage, see package insert). The blood-brain and placenta barriers are only penetrated to a small extent. Excretion is mainly unchanged renally , so that in patients with renal insufficiency an extension of the dosing interval ( clearance <30 ml / min) is necessary.
The pharmacokinetics are concentration-dependent.
There are no significant interactions with the mixed-functional oxidases of the liver ( cytochrome P450 oxidases , CYPs).
application
Daptomycin is only active against Gram-positive bacteria. If mixed infections with Gram-negative and / or certain anaerobic bacteria are suspected, daptomycin should only be used together with appropriate antibiotics. Approved indications are:
- Complicated Skin and Soft Tissue Infections (cSSTI)
- Right-sided infectious endocarditis (RIE) due to Staphylococcus aureus
- Staphylococcus aureus - bacteremia associated with RIE or with cSSTI.
By evaluating the non-interventional studies CORE and EUCORE (CUBICIN Outcome Registry), data are available for the treatment of right and left-sided endocarditis, catheter-associated bacteremia and for the treatment of osteomyelitis .
Daptomycin is not suitable for the treatment of pneumonia because it is inactivated by alveolar surfactant .
Data are available for the treatment of children with daptomycin. Daptomycin is approved for the treatment of infections in children aged 1 to 17 years.
Side effects
Occasional constipation , nausea, injection site reactions and headache occur (each affecting about 5% of those treated).
In very rare cases an increase in CPK ( creatine phosphokinase ) occurs during therapy , which can be tolerated up to 5 times. A further increase suggests skeletal muscle damage. During the testing of the substance in a twice daily dose, increased CPK values were measured in a few patients; in individual cases rhabdomyolysis (dissolution of skeletal muscles) occurred . The increase in CPK is very rarely observed in the once-daily dose. Regular monitoring (once a week) of CPK is recommended during therapy with daptomycin. In addition, if other drugs are administered at the same time that are also associated with an increase in CPK (e.g. HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors, statins ), the CPK should be monitored more closely.
Resistances
Since it is a relatively new drug (approval in Germany 2006), there are still no significant resistance problems to daptomycin. Cross-resistance with other antibiotics currently on the market (12/2009) is seldom observed due to the structure and the novel mechanism of action, which differ from that of other antibiotics . However, a study showing the sensitivity of Staphylococcus aureus to daptomycin in vancomycin-resistant isolates showed that the resistance mechanism, due to the positive net charge of both substances, leads to cross-resistance, which can furthermore lead to therapy failure. Staphylococcus aureus can also acquire resistance to daptomycin through mutations and regulatory adaptation of its cell membrane and cell wall .
Individual evidence
- ↑ La Plante KL, Rybak MJ Daptomycin - a novel antibiotic against Gram-positive pathogens . In: Expert Opin Pharmacother . 2004 Nov; 5 (11): 2321-2331.
- ↑ Anna Müller, Michaela Wenzel, Tanja Schneider, Leendert W. Hamoen et al .: Daptomycin inhibits cell envelope synthesis by interfering with fluid membrane microdomains . In: PNAS . October 24, 2016, doi : 10.1073 / pnas.1611173113 ( pnas.org ).
- ↑ technical information Cubicin.
- ↑ Novartis, since June 1, 2016 MSD SHARP & DOHME: Information for professionals on Cubicin (Daptomycin). (No longer available online.) Novartis, as of June 1, 2016 MSD SHARP & DOHME, November 2015, archived from the original on May 31, 2016 ; accessed on May 31, 2016 . Info: The archive link was inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice.
- ↑ G. Sakoulas, J. Alder, C. Thauvin-Eliopoulos, RC Moellering, GM Eliopoulos: Induction of daptomycin heterogeneous susceptibility in Staphylococcus aureus by exposure to vancomycin. In: Antimicrobial agents and chemotherapy. Volume 50, number 4, April 2006, pp. 1581-1585, doi : 10.1128 / AAC.50.4.1581-1585.2006 , PMID 16569891 , PMC 1426932 (free full text).
- ↑ U. Bertsche, SJ Yang, D. Kuehner, S. Wanner, NN Mishra, T. Roth, M. Nega, A. Schneider, C. Mayer, T. Grau, AS Bayer, C. Weidenmaier: Increased cell wall teichoic Acid production and D-alanylation are common phenotypes among daptomycin-resistant methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) clinical isolates. In: PloS one. Volume 8, number 6, 2013, p. E67398, doi : 10.1371 / journal.pone.0067398 , PMID 23785522 , PMC 3681945 (free full text).
Trade names
Daptomycin is commercially available in Europe, Australia, Brazil and the USA under the name Cubicin.
Web links
- Daptomycin - a new therapy option for infections with gram-positive (problem) germs (Zeitschrift für Chemotherapie, No. 4, Berlin 2006)
- Recommendations for the use of daptomycin in severe infections (IntensivNews 2009)
- Treatment options for severe infections caused by gram-positive pathogens (Chemotherapy Journal 2009)
literature
- Steenbergen, JN, et al. (2005): Daptomycin: a lipopeptide antibiotic for the treatment of serious Gram-positive infections. In: J. Antimicrob. Chemother. Vol. 55, pp. 283-288. PMID 15705644 PDF .
- VG Fowler et al .: Daptomycin versus standard therapy for bacteremia and endocarditis caused by Staphylococcus aureus. In: New England Journal of Medicine. Volume 335, 2006, pp. 653-665.