Dassault Mirage 5
| Dassault Mirage 5 | |
|---|---|

|
|
| Type: | Single seat tactical fighter aircraft |
| Design country: | |
| Manufacturer: | |
| First flight: |
May 19, 1967 |
| Commissioning: |
May 1968 |
| Production time: |
1967 to 1992 |
| Number of pieces: |
592 (including 61 IAI Nescher ) |
The Dassault Mirage 5 (sometimes incorrectly referred to as the Mirage V) is an export variant of the Mirage III E from the same manufacturer. In contrast to the Mirage III fighter aircraft , the Mirage 5 is primarily designed as a ground attack aircraft.
development
Three years after the first delivery of the Mirage III, Israel ordered a special version of the then ultra-modern fighter aircraft from Dassault. The good weather conditions in the region made the complex electronics of the Mirage III superfluous. An aircraft with the same flight characteristics as the Mirage III, but without the complexity was required. But an arms embargo imposed by France after the Six Day War prevented the delivery of the fifty machines on order to Israel. Since the embargo also affected spare parts deliveries and the Israeli air force urgently needed new aircraft, Israel was forced to procure the necessary parts independently of France. With the help of the Swiss engineer Alfred Frauenknecht, the Israelis obtained aircraft construction plans for the Mirage III and began manufacturing the IAI Nescher in 1971 .
construction
Compared to the original model, the Mirage 5 is 450 kg lighter, cheaper and far more maintenance-friendly. By eliminating a large part of the electronics, an additional 500 l fuel tank could be installed behind the cockpit. In addition, additional weapon stations were installed. Despite the changes, the Mirage 5 is practically identical to the previous model.
User states
-
 Argentina : (10 Mirage 5P3 / P4 from Peru, 43 IAI Nesher from Israel, retired in 2015)
Argentina : (10 Mirage 5P3 / P4 from Peru, 43 IAI Nesher from Israel, retired in 2015) -
 Egypt : 82 (16 Mirage 5E2, 54 Mirage 5SDE, 6 Mirage 5SDR, 6 Mirage 5SDD)
Egypt : 82 (16 Mirage 5E2, 54 Mirage 5SDE, 6 Mirage 5SDR, 6 Mirage 5SDD) -
 Belgium : 106 (63 Mirage 5BA, 27 Mirage 5BR, 16 Mirage 5BD, all retired in 1993, 25 sold to Chile)
Belgium : 106 (63 Mirage 5BA, 27 Mirage 5BR, 16 Mirage 5BD, all retired in 1993, 25 sold to Chile) -
 Chile : 17 (6 Mirage 50C, 8 Mirage 50FC, 3 Mirage 50DC, retired from 2006–2007)
Chile : 17 (6 Mirage 50C, 8 Mirage 50FC, 3 Mirage 50DC, retired from 2006–2007) -
 Democratic Republic of the Congo : 8 Mirage 5M, 3 Mirage 5DM, all retired.
Democratic Republic of the Congo : 8 Mirage 5M, 3 Mirage 5DM, all retired. -
 Ecuador : 6 Mirage 50s, all retired
Ecuador : 6 Mirage 50s, all retired -
 France : 50 Mirage 5F, all retired
France : 50 Mirage 5F, all retired -
 Gabon : 9 (3 Mirage 5G, 4 Mirage 5DG, 2 Mirage 5M, all retired)
Gabon : 9 (3 Mirage 5G, 4 Mirage 5DG, 2 Mirage 5M, all retired) -
 Israel : 61 IAI Nescher (all retired, 43 sold to Argentina)
Israel : 61 IAI Nescher (all retired, 43 sold to Argentina) -
 Colombia : 18 (14 Mirage 5COA, 2 Mirage 5COD and 2 Mirage 5COR, all retired)
Colombia : 18 (14 Mirage 5COA, 2 Mirage 5COD and 2 Mirage 5COR, all retired) -
 Libya : 110 (53 Mirage 5D, 32 Mirage 5DE, 10 Mirage 5DR, 15 Mirage 5DD, all retired, 50 sold to Pakistan)
Libya : 110 (53 Mirage 5D, 32 Mirage 5DE, 10 Mirage 5DR, 15 Mirage 5DD, all retired, 50 sold to Pakistan) -
 Pakistan : 151 (28 Mirage 5PA, 4 Mirage 5DPA, 18 Mirage 5PA2, 18 Mirage 5PA3, 33 Mirage 5F, 50 Mirage 5 from Libya) should all be retired by 2025.
Pakistan : 151 (28 Mirage 5PA, 4 Mirage 5DPA, 18 Mirage 5PA2, 18 Mirage 5PA3, 33 Mirage 5F, 50 Mirage 5 from Libya) should all be retired by 2025. -
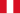 Peru : 40 (22 Mirage 5P, 10 Mirage 5P3, 2 Mirage 5P4, 4 Mirage 5DP, 2 Mirage 5DP3)
Peru : 40 (22 Mirage 5P, 10 Mirage 5P3, 2 Mirage 5P4, 4 Mirage 5DP, 2 Mirage 5DP3) -
 Venezuela : 4 Mirage 5V, 2 Mirage 5DV, 13 Mirage 50EV, 3 Mirage 50DV, retired in 2009.
Venezuela : 4 Mirage 5V, 2 Mirage 5DV, 13 Mirage 50EV, 3 Mirage 50DV, retired in 2009. -
 United Arab Emirates : 17 (3 Mirage 5DAD + 14 Mirage 5EAD, all retired and sold to Pakistan)
United Arab Emirates : 17 (3 Mirage 5DAD + 14 Mirage 5EAD, all retired and sold to Pakistan)
Technical specifications
| Parameter | Mirage 5 data |
|---|---|
| Type | single seat tactical fighter aircraft |
| crew | 1 |
| length | 15.55 m |
| span | 8.22 m |
| Wing area | 34.9 m² |
| height | 4.50 m |
| Max. Gun load | 4,200 kg |
| Empty mass | 6,600 kg |
| normal take-off mass as an interceptor | 10,000 kg |
| Max. Takeoff mass | 13,500 kg |
| internal fuel capacity | 3,830 l |
| Top speed | (without external loads)
|
| Cruising speed at 11,000 m | 956 km / h |
| Service ceiling | 18,500 m |
| Max. Climb rate from NN to 11,000 m | 186 m / s |
| Transfer range with three additional tanks | 4,000 km |
| Deployment radius deep-deep-deep | 435 km |
| Operating radius for intercepting at high altitudes | 325 km |
| Operational radius long-range interceptor | 1,300 km |
| Wing loading | 393 kg |
| Take-off run with normal weapon load | 1,450 m |
| Landing run without a landing screen | 1,620 m |
| Engine | a SNECMA Atar 09C-3 jet engine |
| Thrust |
|
Armament
- Guns integrated in the fuselage
- 2 × 30 mm M553 DEFA revolver automatic cannon with 125 rounds of ammunition each, permanently installed on-board armament
Ordnance up to 4,200 kg at seven external load stations under the two wings and under the fuselage
Air-to-air guided missile
- 2 × launch rails for 1 × Matra R.550 Magic 1/2 each - infrared-controlled short-range air-to-air guided missile
- 2 × LAU-7 / A launch rails for 1 × Philco-Ford AIM-9P Sidewinder each - infrared -controlled short-range air-to-air guided missile
Unguided air-to-surface missiles
- 2 × Matra JL-100 rocket launchers, each with 19 × unguided SNEB air-to-surface missiles, caliber 68 mm; combined with a drop tank for 250 liters (66 US gallons) of kerosene
Unguided bombs
- 6 × SAMP EU2 (250 kg free-fall bomb ; analogous to Mk.82)
- 3 × SAMP T200 (400 kg free-fall bomb; analogous to Mk.83)
Additional container
- 2 × disposable additional tanks for 625 liters of kerosene
Self-defense systems
- 1 × Philips-Matra Phimat decoy launcher with 210 chaff cartridges
Comparable types
- Mirage III
- Northrop F-5
- Chengdu J-7
- Mikoyan-Gurevich MiG-21
- Sukhoi Su-7
- Sukhoi Su-9
- Sukhoi Su-11
- IAI Kfir
- IAI Nescher
See also
literature
- William Green: Planes in the world today - tomorrow. Werner Classen Verlag, Zurich / Stuttgart 1974.
- Günter Endres, Michael J. Gething: Jane's Aircraft Recognition Guide, fifth Edidion, HarperCollins Publishers. London 2007, ISBN 978-0-00-725792-8 .
- Bill Gunston, Mike Spick: Modern warplanes, technology, tactics and armament. Motorbuch Verlag, Stuttgart 1998.

