Demoxepam
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|

|
||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Demoxepam | |||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 15 H 11 ClN 2 O 2 | |||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
light yellow odorless solid |
|||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 286.71 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
|||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
235-240 ° C |
|||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| Toxicological data | ||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||||||||
Demoxepam is a chemical compound from the group of benzodiazepines . It is also one of the primary metabolites of chlordiazepoxide .
Extraction and presentation
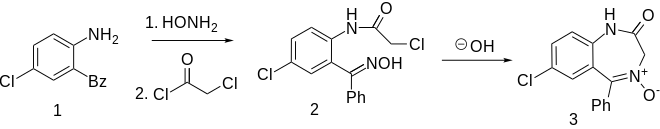
Demoxepam can be obtained by a multi-stage reaction starting from 4-chloroaniline ( 1 ) via 2-amino-5-chlorobenzophenone ( 3 ) and other intermediate products.
use
Demoxepam is a psychotropic agent from the class of benzodiazepines, which have a muscle-relaxing and amnestic effect. The plasma half-life in humans varies between 14 and 95 hours. This converts to a large number of different metabolites. It is used as an intermediate in the manufacture of oxazepam .
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e lgcstandards: Demoxepam- CAS Number 963-39-3 , accessed on January 26, 2019
- ↑ This substance has either not yet been classified with regard to its hazardousness or a reliable and citable source has not yet been found.
- ↑ Data sheet Demoxepam solution, 1.0 mg / mL in acetonitrile, ampule of 1 mL, certified reference material from Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on January 26, 2019 ( PDF ).
- ↑ Google Patents: US3136815A - Amino substituted benzophenone oximes and derivatives thereof , accessed January 26, 2019.
- ^ Fv Bruchhausen, S. Ebel, AW Frahm, E. Hackenthal: Hager's handbook of pharmaceutical practice substances AD . Springer-Verlag, 2013, ISBN 978-3-642-57995-0 , pp. 1197 ( limited preview in Google Book Search).
- ^ Morton A. Schwartz, Edward Postma: Metabolites of Demoxepam, a Chlordiazepoxide Metabolite, in Man. In: Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences. 61, 1972, p. 123, doi : 10.1002 / jps.2600610128 .
- ^ Maxwell Gordon: Psychopharmacological Agents . Elsevier, 2012, ISBN 978-0-323-15128-3 , pp. 190 ( limited preview in Google Book Search).