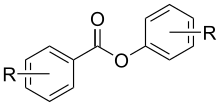
Depside
Depside (from Greek dépsein “to soften”, “knead”) are condensation products of aromatic hydroxycarboxylic acids in which the carboxyl group of one acid is esterified with a phenolic hydroxyl group of the other ( didepside ); three ( tridepsis ) or more hydroxycarboxylic acid molecules can also be involved.
Occurrence
Depside occur in lichens (e.g. in Lecanoromycetes such as oak moss or Lecanora conizaeoides ), as vegetable tannins (e.g. in savory ; digallic acid ), in rosemary ( rosemary acid , widely used in plants) or in coffee ( chlorogenic acid , also in a number of plants).
Biological effect
Depside have a molluscicidal effect on freshwater snails and, in concentrations of 10 −3 mol · l −1, inhibit growth against plants.
literature
- Entry to Depside. In: Römpp Online . Georg Thieme Verlag, accessed on January 2, 2015.
Individual evidence
- ↑ Wolfgang Legrum: Fragrances, between stink and fragrance , Vieweg + Teubner Verlag (2011) pp. 140-141, ISBN 978-3-8348-1245-2 .