Dihalomethanes
The dihalomethanes are organic compounds in which two hydrogen atoms in the methane are replaced by halogens . Dihalomethanes belong to the haloalkanes or to the subgroup of halomethanes .
Representative
| Structural formula |
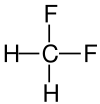
|

|
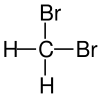
|

|
| Surname | Difluoromethane | Dichloromethane | Dibromomethane | Diiodomethane |
| Melting point | −136 ° C | −97 ° C | −52 ° C | 6 ° C |
| boiling point | −51.7 ° C | 40 ° C | 97 ° C | decomposition |
| Dome model |

|

|
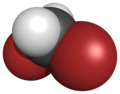
|
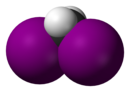
|
The corresponding dihalomethanes of all halogens are known: difluoromethane, dichloromethane, dibromomethane, diiodomethane.
There are also six dihalomethanes of the type CH 2 XY, where X and Y are different halogens:
- Bromochloromethane
- Bromofluoromethane
- Bromiodomethane
- Chlorofluoromethane
- Chloroiodomethane
- Fluoroiodomethane
See also
Web links
Commons : Dihalomethanes - collection of images, videos and audio files
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b Entry on difluoromethane in the GESTIS substance database of the IFA , accessed on February 29, 2020(JavaScript required) .
- ↑ a b Entry on dichloromethane in the GESTIS substance database of the IFA , accessed on February 29, 2020(JavaScript required) .
- ↑ a b Entry on dibromomethane in the GESTIS substance database of the IFA , accessed on February 29, 2020(JavaScript required) .
- ↑ a b Entry on methylene iodide in the GESTIS substance database of the IFA , accessed on February 29, 2020(JavaScript required) .