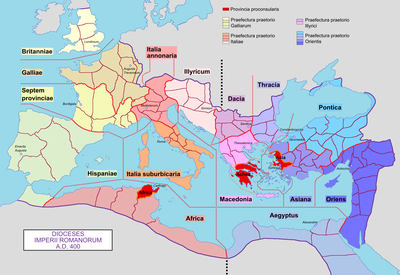
Dioecesis Asiana
The Dioecesis Asiana (Greek: Διοίκησις Ασίας / Ασιανής ) was a late antique administrative unit ( Dioecesis ) of the Roman or Eastern Roman Empire . It existed from 314 to 535 AD. The main place was Ephesus .
Territory structure
The Dioecesis Asiana comprised the following 9 provinces:
- [Lycia et] Pamphylia
- Phrygia great
- Phrygia secunda
- Asia
- Lydia
- Caria
- Insulae
- Pisidia
- Hellespontus
history
The Roman Empire was initially divided into 46 provinces , which Diocletian essentially increased to 101 provinces by dividing around 300 AD, which in turn were combined into dioceses. The head of the dioceses (and provinces) was the vicarius , deputy of the civil officer who emerged from the military praetorian prefect after 312 . Already with the division of the empire in 395 , the structure of the dioceses was changed into four prefectures, 15 dioceses and 119 provinces. From this point on, the diocese was subordinate to the Prafectus praetorio per Orientem . The late antique diocesan structure was only abandoned in favor of the thematic constitution in view of the Islamic expansion (from 630) .
List of known Vicarii Asiae
- Flavius Ablabius (324–326)
- Tertullianus (approx. 330)
- Veronicianus (334-335)
- Scylacius (approx. 343)
- Anatolius (c. 352)
- Araxius (353-354)
- Germanus (360)
- Italicianus (361)
- Caesarius (362-363)
- Clearchus (363-366)
- Auxonius (366-367)
- Musonius (367-368)
literature
- Timothy David Barnes: The new empire of Diocletian and Constantine. Harvard University Press, Cambridge (MA) 1982, ISBN 0-674-61126-8 , pp. 201-208.
- Theodor Mommsen : Directory of the Roman provinces drawn up around 297. In: Treatises of the Berlin Academy of Sciences. Phil.-hist. Class . 1862, pp. 489-518 ( digitized version ).
- Otto Seeck : Notitia dignitatum: accedunt Notitia urbis Constantinopolitanae et laterculi provinciarum. Weidmann, Berlin 1876, pp. 247-251 ( digitized version ).