Phrygia
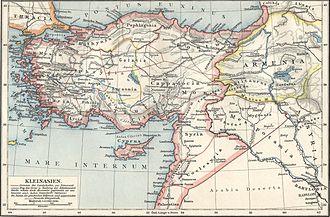
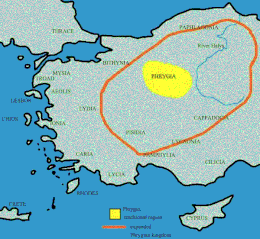
Phrygia ( ancient Greek Φρυγία ) is the ancient name of a region in western Central Asia Minor in what is now Turkey . This landscape is named after the Phrygians , among whom Phrygia was the heartland of a great empire in Anatolia that was founded in the 8th century BC. BC reached the height of his power under King Midas .
geography
Phrygia bordered Cappadocia to the east, Pisidia and Lycaonia to the south, Lydia to the west, and Bithynia and Paphlagonia to the north-west and north .
The most important city in Phrygia was Gordion , located on the Sangarios River (now Sakarya ), 80 kilometers west-southwest of Ankara . Kelainai , located in the south of Phrygia, served the great Persian kings as a royal seat and was the most important market town in Asia Minor after Ephesus in Roman times. In late antiquity, the capital Kolossai , to whose Christian community the apostle Paul wrote a letter, was mentioned.
history
The Phrygians settled in the 12th century BC. BC , coming from Troas and Thrace , arrive in this landscape. This region had previously belonged to the Hittite empire . Beginning of the 7th century BC BC the Cimmerians invaded Phrygia and conquered Gordion. The Phrygian culture persisted for a long time.
End of the 7th century BC Phrygia became increasingly dependent on the Lydians . From 546 to 334 BC It belonged to the Persian Empire . In winter from 334 to 333 BC Chr. Was Alexander the Great to Phrygia. During his stay he is said to have broken the legendary Gordian knot .
Around 274 BC Chr. Were Celtic Galatians from the Diadochenherrscher Antiochus I Soter located in the eastern part of Phrygia. This area was soon named Galatia after them. Around the middle of the 1st century BC Chr. Phrygia became Roman and from then on belonged to the province Asia . Galatia was a Roman client state and was only annexed to the Roman Empire under the principle of Augustus .
Ruler
According to Herodotus , Histories 1,14,35; 41-45 and Strabon , Geographica 1,3,21.
| Reign | Surname | genealogy | Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gordios (I.) | |||
| 1st half of 7th century BC Chr. (?) | Midas | son | Suicide on the occasion of a Kimmeri incursion (possible around 668, 657 or 644) |
| Gordios (II.) | son |
religion
In Phrygia the cult of the Great Mother Cybele and the wine god Sabazios , which is related to Dionysus , who was documented in Mycenaean times , was of importance. Cybele was later also worshiped by the Romans, where she was called Magna Mater deorum Idaea .
See also
literature
- Klaus Belke , Norbert Mersich: Phrygia and Pisidia ( Tabula Imperii Byzantini Vol. 7). Publishing house of the Austrian Academy of Sciences, Vienna 1990. ISBN 3-7001-1698-5
- Christian Marek : History of Asia Minor in Antiquity. CH Beck, Munich 2010, pp. 144–151 (Chapter: 3.4 Phrygians (approx. 11th to 6th centuries BC) ), 922 (Index Phrygians / Phrygien ).