Diphthamide
| Structural formula | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
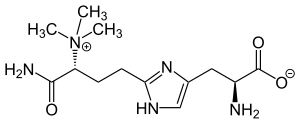
|
|||||||||||||
| L -diphthamide | |||||||||||||
| General | |||||||||||||
| Surname | Diphthamide | ||||||||||||
| other names |
|
||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 13 H 23 N 5 O 3 | ||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | |||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||
| properties | |||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 297.35 g mol −1 | ||||||||||||
| safety instructions | |||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | |||||||||||||
Diphthamide is a histidine- derived amino acid that only plays a role in one elongation step in protein biosynthesis . Further biological functions and an occurrence outside of protein biosynthesis are not known. The name is derived from diphtheria toxin , the inhibiting effect of which is based on the diphthamide. The comparable toxins exotoxin A and cholera toxin also act on the diphthamide.
During elongation in eukaryotes and archaea , the elongation factor 2 (EF-2) required for this contains the diphthamide derived therefrom in its peptide chain at one position instead of the amino acid histidine. The biosynthesis is complex, at least seven proteins are involved. In the course of the biosynthesis, the histidine is modified to the diphthamide in the form built into the peptide chain .
The 3-amino-3-carboxypropyl group from S-adenosylmethionine is transferred to the histidine as a radical . A methyl transferase then catalyzes the trimethylation and a synthase an amidation .
Individual evidence
- ↑ This substance has either not yet been classified with regard to its hazardousness or a reliable and citable source has not yet been found.
- ^ Rolf Knippers: Molecular Genetics. Georg Thieme Verlag, 2006, ISBN 978-3-134-77009-4 , p. 445 ( limited preview in the Google book search).
- ↑ Daniel Ladant: The Comprehensive Sourcebook of Bacterial Protein Toxins. Academic Press, 2005, ISBN 978-0-080-45698-0 , p. 250 ( limited preview in Google Book Search).
- ^ Biosynthesis in baker's yeast
- ^ Damien M. Murphy: Electron Paramagnetic Resonance. Royal Society of Chemistry, 2010, ISBN 978-1-847-55061-3 , p. 138 ( limited preview in Google book search).
- ^ Georges N. Cohen: Microbial Biochemistry. Springer Science & Business Media, 2011, ISBN 978-9-048-19437-7 , p. 407 ( limited preview in Google book search).
- ^ S. Liu, GT Milne et al. a .: Identification of the proteins required for biosynthesis of diphthamide, the target of bacterial ADP-ribosylating toxins on translation elongation factor 2. In: Molecular and cellular biology. Volume 24, Number 21, November 2004, pp. 9487-9497, ISSN 0270-7306 . doi : 10.1128 / MCB.24.21.9487-9497.2004 . PMID 15485916 . PMC 522255 (free full text).