Diundecyl phthalate
| Structural formula | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
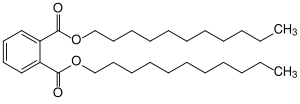
|
||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||
| Surname | Diundecyl phthalate | |||||||||
| other names |
|
|||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 30 H 50 O 4 | |||||||||
| Brief description |
yellowish liquid with a faint odor |
|||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||
|
||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||
| Molar mass | 474.72 g mol −1 | |||||||||
| Physical state |
liquid |
|||||||||
| density |
0.9527 g cm −3 |
|||||||||
| Melting point |
−40 ° C |
|||||||||
| boiling point |
336 ° C |
|||||||||
| Vapor pressure |
0.79 hPa (200 ° C) |
|||||||||
| solubility |
|
|||||||||
| Refractive index |
1.48 (20 ° C) |
|||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||
|
||||||||||
| Toxicological data | ||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . Refractive index: Na-D line , 20 ° C | ||||||||||
Diundecyl phthalate is a chemical compound from the group of phthalic acid esters .
Extraction and presentation
Diundecyl phthalate can be obtained by reacting phthalic anhydride with undecanol .
properties
Diundecyl phthalate is a flammable, difficult to ignite, yellowish liquid with a faint odor that is practically insoluble in water.
use
Diundecyl phthalate is used as a plasticizer for PVC.
Risk assessment
In 2014, diundecyl phthalate was included in the EU's ongoing action plan ( CoRAP ) in accordance with Regulation (EC) No. 1907/2006 (REACH) as part of substance evaluation . The effects of the substance on human health and the environment are re-evaluated and, if necessary, follow-up measures are initiated. The reasons for the uptake of diundecyl phthalate were concerns about high (aggregated) tonnage and the dangers arising from a possible assignment to the group of CMR substances. The re-evaluation has been running since 2014 and is carried out by Denmark .
literature
- Toxicity review for diundecyl phthalate (DUP, CAS number: 3648-20-2) , Prepared for US Consumer Product Safety Commission, June 29, 2011.
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e f g h i Entry on diundecyl phthalate in the GESTIS substance database of the IFA , accessed on June 17, 2017(JavaScript required) .
- ↑ a b c d Anna Wypych: Databook of Plasticizers . Elsevier, 2017, ISBN 978-1-927885-15-4 , pp. 536 ( limited preview in Google Book search).
- ^ GWA Milne: Gardner's Commercially Important Chemicals Synonyms, Trade Names, and Properties . John Wiley & Sons, 2005, ISBN 0-471-73661-9 , pp. 251 ( limited preview in Google Book search).
- ↑ entry to diundecylphthalate in the Hazardous Substances Data Bank , accessed on 17 June 2017th
- ↑ Werner Baumann, Thomas Rothardt: Printing chemicals data and facts on environmental protection 2nd, expanded and revised edition . Springer-Verlag, 2013, ISBN 978-3-642-58474-9 , pp. 585 ( limited preview in Google Book search).
- ↑ Victor O. Sheftel: Indirect Food Additives and Polymers Migration and Toxicology . CRC Press, 2000, ISBN 978-1-56670-499-1 , pp. 270 ( limited preview in Google Book search).
- ↑ Community rolling action plan ( CoRAP ) of the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA): Diundecyl phthalate, branched and linear , accessed on March 26, 2019.