Douglas A-3
| Douglas A3D / A-3 Skywarrior | |
|---|---|
 An A3D-1 of the VAH-3 of the USS Franklin D. Roosevelt |
|
| Type: | bomber |
| Design country: | |
| Manufacturer: | |
| First flight: |
October 28, 1952 |
| Commissioning: |
1956 |
| Production time: |
1956 to 1961 |
| Number of pieces: |
282 |
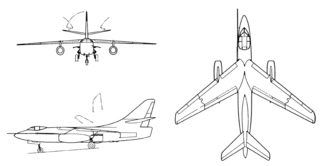
The Douglas A-3 Skywarrior (before 1962 A3D) was a twin-engined fighter aircraft of the Cold War era from American production. It was the heaviest and longest in service carrier aircraft in the US Navy . The manufacturer was the Douglas Aircraft Company .
development
The "Skywarrior" Project for a supported, nuclear-capable bombers began in 1947. But the planning of the basic design lasted two years, so Douglas got the official construction contract in March 1949. The two-seater aircraft was a monoplane swept with 36 ° and foldable wings and planned below hanging jet engines . The cell had a weapon bay for dropping ammunition and a radar-controlled bomb drop device. A remote-controlled 20 mm twin automatic cannon was installed in the stern as defensive armament . Two Westinghouse XJ40-WE-3 turbojets with 3,175 kp of thrust should be used as propulsion . The maiden flight took place on October 28, 1952. But constant engine problems and the discontinuation of the development of the XJ40 led to the decision to install the Pratt & Whitney J57 engine. With this more reliable and more powerful engine, the prototype of the XA3D-1 flew for the first time on September 16, 1953. In an emergency, the crew should leave the aircraft independently and jump with parachutes, as no rescue system with ejector seats was installed. Similar to the F3D fighter, this was to be made easier for the crew by a tunnel slide leading from the cabin to the emergency exit.
Of the first production version, the A3D-1, only 50 were built and only came to the task force in March 1956. There they were also nicknamed Whale (whale) because of their enormous size compared to the earlier carrier aircraft. After the introduction of the improved A3D-2, the A3D-1 aircraft were used in training.

The actual operational model was then the A3D-2, which was equipped with better avionics in addition to the more powerful J57-P-10 engine with 4,763 kp without and 5,625 kp with water injection . With this equipment, the bomber was the first carrier aircraft to be capable of all weather operations. The bombs could then be dropped manually, semi-automatically and fully automatically; this improved the likelihood of a successful use of weapons and also the survivability of the aircraft.
When the A3D-2 was renamed A-3B in 1962 as part of the standardization of the designation, the avionics were also modernized. In addition, the automatic cannons were expanded and exchanged for radar jammers and decoys .
In the early 1960s, the successor North American A-5 Vigilante came along with the decision to move the Navy's "nuclear deterrent" from aircraft carriers to the nuclear submarine fleet . This enabled the "Skywarrior" to be used for other types of use. First the aircraft were used as a carrier-supported tanker (code KA-3B) by equipping the bomb bay with an air refueling system . They were also used in electronic warfare . Selected specimens with a low number of flying hours were completely rewired and given a four-seater cabin. The additional crew members operated a variety of radar reconnaissance and combat equipment. These EA-3Bs remained in service throughout the Vietnam War and the following two decades until the Gulf War . From 1989 it was replaced by the Grumman EA-6B Prowler . The last EA-3B was retired in September 1991.
The United States Air Force used a variant known as the B-66 Destroyer .
variants
- YA-3A (XA3D-1)
- Two prototypes, the first with J40 engines, the second with J57 engines.
- A-3A (A3D-1)
- 50 machines; Production aircraft.
- YRA-3A (YA3D-1P)
- Prototype of a reconnaissance aircraft, conversion from A-3A.
- YEA-3A (YA3D-1Q)
- Prototype of an ECM version, conversion from A-3A.
- EA-3A (A3D-1Q)
- ECM version, conversion from A-3A.
- A-3B (A3D-2)
- Production version with reinforced airframe, larger bomb bay and J57-10 engines, 164 built.
- YEA-3B (YAeD-2Q)
- Prototype of an ECM version, 1 built.
- EA-3B (A3D-2Q)
- ECM and Elint version, 24 machines built.
- KA-3B
- Conversion of 85 A-3B to tanker aircraft from 1967, expansion of the armament and the bomb target radar (thereby new aircraft nose).
- EKA-3B
- Conversion of 34 KA-3B and five A-3B to tanker aircraft with ECM equipment, dismantling to KA-3B from 1972.
- RA-3B (A3D-2P)
- Photo reconnaissance aircraft, built 30 machines.
- ERA-3B
- ECM-equipped RA-3B.
- TA-3B (A3D-2T)
- School machine as a navigation and bomb target trainer, 12 machines built.
- UA-3B
- Conversion of two TA-3B to VIP transporters.
- VA-3B
- Conversion of an EA-3B into a VIP transporter.
- various machines were converted for test purposes and designated as NRA-3A, NA-3A, NRA-3B and TNRA-3B.
Technical data of the A-3B Skywarrior
- Type: carrier-based light bomber
- Engine: two Pratt & Whitney J57 -P-10 turbojet engines with 4,763 kp thrust without and 5,625 kp with water injection
- Performance: top speed at 3,050 m altitude 982 km / h; Service ceiling 12,495 m; Operational radius with standard fuel tank 1,690 km; Max. Range 4,667 km
- Weight: curb weight 17,876 kg; Standard takeoff weight 31,752 kg; Max. Takeoff weight 37,195 kg
- Dimensions: span 22.10 m; Length 23.27 m; Height 6.95 m; Wing area 75.43 m²
Armament
- Rear armament for self-defense
- 2 automatic cannons in caliber 20 mm of the type Hispano-Suiza HS.404 (in the American armed forces as M3, in the US Air Force as M24) with 400 rounds of ammunition each. The automatic cannons are installed on a double mount in a movable dome at the rear. A separate fire control radar, also built into a dome at the stern, was used for aiming; the gunner / navigator operated the weapon by remote control.
- Explosive ordnance up to 5,443 kg in the internal bomb bay and two external load stations under the wings
- Unguided bombs
- 1 × Mk.15 Mod. 2 (Parachute-delayed free-fall bomb with thermonuclear 1.69 / 3.8 MT explosive device)
- 12 × BLU-111A / B (227 kg / 500 lb free-fall bomb, analogous to Mk.82 with thermal protective coating)
- 6 × BLU-110 / B (454 kg / 1000 lb free-fall bomb , analogous to Mk.83)
- 6 × AN-Mk. 1 armor-piercing 730 kg free fall bomb (1,600 lb)
- 4 × BLU-109 / B (907 kg / 2000 lb free-fall bomb, analogous to Mk.84)
- 6 × Mk.36 "Destructor" (250 kg / 560 lb sea mine based on the Mk.82 Snakeye)
- 6 × Mk.25 Mod. 2 (900 kg / 2000 lb sea mine)
Web links