Yew-leaved nut slice
| Yew-leaved nut slice | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|

Branches of the yew-leaved nut ( Torreya taxifolia ) |
||||||||||||
| Systematics | ||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||
| Scientific name | ||||||||||||
| Torreya taxifolia | ||||||||||||
| Arn. |
The Torreya taxifolia or Florida Nutmeg ( Torreya taxifolia ) is a species of the genus of Torreya ( Torreya ) in the family of Yews (Taxaceae). It occurs only in the southern US states of Florida and Georgia and is "critically endangered".
description
Vegetative characteristics
The yew-leaved nut wedge is an evergreen tree that can grow to heights of around 15 to 20 meters and a trunk diameter ( breast height diameter , BHD) of 80 centimeters. The wide spreading branch and the strong, conical crown are striking . Even in the stand, the trunk remains branched to the base. Younger branches are yellowish-green, yellowish-brown or gray. The bark is brown to gray-brown in color and has flat cracks and interwoven elevations.
The 1.5 to 3.8 centimeters long leaves are stiff and have sharp, piercing tips. On the upper side the needles have a glossy dark green color, on the underside they are a little lighter, the stomatal ligaments are hardly noticeable. The needles give off a very aromatic odor that is also perceived as unpleasant. That is why it is also called "stinking cedar" in English.
Generative characteristics
The yew-leaved nut slice is dioecious, separate sexes ( diocesan ). The male cones are pale yellow. The seed is located in a gray-green to dark green, purple-grained seed coat ( arillus ). The seed with the seed coat is a total of 2.5 to 3.5 inches long and 1.5 inches wide. The seeds need a dormancy of around 9 to 18 months before germination .
Occurrence and endangerment
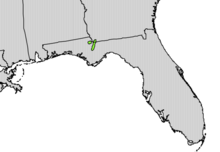
The natural distribution area of the yew-leaved nut is in the US states of Florida and Georgia and is restricted to the east side of the Apalachicola River . The area covers around 200 km² and has steep slopes 30 to 60 meters high, mainly made of limestone . The climate is humid and temperate , with occasional winter temperatures just below freezing.
Yew-leaved nut slices grow as an undergrowth, mixed with Fagus grandifolia , Liriodendron tulipifera , Acer barbatum , Liquidambar styraciflua , and Quercus alba as well as the also rare yew species Taxus floridana .
The population of this species has declined by 98% since the 1950s and now consists of only about 500 individuals. It is known that cones are formed from only 10 fully-grown tree specimens. The reasons for the decline are the current subject of research. A fungus from the genus Fusarium , which causes trees to die off before they fructify , could be one of the culprits.
Due to the decline in population and the lack of natural regeneration, extinction in the wild is to be expected. A private initiative by conservationists is trying to establish ex-situ populations of the yew-leaved nut-yew by sowing seeds in more northerly and higher altitudes, as it is believed that the warming caused by post-glacial climate change may have made it impossible for the species to grow in its natural range to survive.
Taxonomy
The first description of Torrey taxifolia was described in 1838 by George Arnott Walker Arnott , who also set up the genus Torreya in the same article . The generic name Torreya honors John Torrey . The specific epithet taxifolia means with yew leaves . Synonyms for Torreya taxifolia Arn. are Tumion taxifolium Arn. Greene and Taxus montana Nutt.
use
In the first half of the 20th century, the wood was used for shingles , fence posts and boat building due to its good resistance to fungus degradation .
The wood is yellow and has a fine texture.
swell
- Christopher J. Earle: Torreya taxifolia. In: The Gymnosperm Database. December 14, 2010, accessed on November 17, 2011 (English, sections description, distribution and systematics).
- Schütt (Ed.) Et al .: Lexicon of Conifers . 1st edition. Nikol-Verlag, Hamburg 2004 (special edition), ISBN 3-933203-80-5 .
- Matthew H. Hils: Torreya taxifolia . In: Flora of North America Editorial Committee (Ed.): Flora of North America North of Mexico . Volume 2: Pteridophytes and Gymnosperms . Oxford University Press, New York / Oxford a. a. 1993, ISBN 0-19-508242-7 (English).
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d Torreya taxifolia in the Red List of Threatened Species of the IUCN 2011. Posted by: T. Spector, R. Determann, M. Gardner, 2011. Retrieved on November 17, 2011.
- ↑ Efforts to Save Torreya taxifolia. torreyaguardians.org, accessed November 17, 2011 .
- ^ GAW Arnott: On the Genus Torreya . In: Annals of natural history . tape 1 , no. 2 , 1838, p. 126–132 ( page 130ff, scanned from biodiversitylibrary.org [accessed November 17, 2011]).
- ↑ Torreya taxifolia at Tropicos.org. Missouri Botanical Garden, St. Louis, accessed November 17, 2011.}