Electron beam technology
The electron beam technology is a branch of electrical engineering.
description
Applications and operating principles based on the targeted technical emission of electrons . The electron serves as an energy source for a physically or chemically effective process. The electron is then either used as an information- transmitting medium for a projection (optics) or acts as an energy-transmitting medium in process engineering applications on a target substrate. There are various industrial and scientific fields of application and a constantly evolving theory that goes back to physics at the end of the 19th century.
Working principle
There are several functional principles to supply enough energy to the cathode , the emitting body, so that electrons can be emitted, whereby the specific, material- dependent work function of the electrons must be achieved. The emitting body wears depending on the emission intensity. These principles are:
- Field emission based on electric field strength
- Glow emission , also referred to as thermionic emission in English-language literature, based on thermal energy (see Edison-Richardson effect ), including field-enhanced glow emission (see Schottky effect )
- Secondary emission based on primary electron bombardment
- Gas discharge / plasma-excited emission, based on bombardment by ionized gases
- Photoemission based on radiation from photons (see photoelectric effect )
All of these principles are characterized by specific areas of application and have different characteristics.
Physical basics
- Edison-Richardson effect (emission of electrons)
- Schottky effect (emission of electrons)
- Peak discharge (emission of electrons)
- Tunnel effect (emission of electrons)
- Field emission (emission of electrons)
- Plasma (physics) (emission of electrons in vacuum or ionized gas)
- Meissner circuit (emission of electrons)
- Boersch effect (emission of electrons)
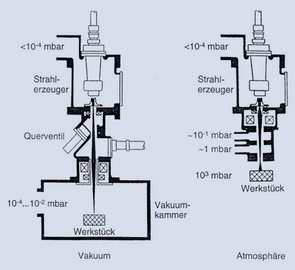
- Vacuum technology (stabilization of electrons, free flight)
- Optoelectronics (stabilization of electrons, focusing)
- Electron optics (stabilization of electrons, focusing)
Common components
- Cathode (emission source)
- Cathode ray tube (emission chamber)
- Fluorescent display (projection surface)
- Electron tube (emission chamber)
- Magnetron (emission source)
- Vacuum chambers for the work process
history
Essential foundations were laid with the Braun electron tube after the invention of the light bulb by Edison. This was used, among other things, in broadcast technology. Manfred von Ardenne further developed the technology and made it applicable to the electron microscope and, after the war, for welding , evaporation , cutting (manufacturing technology) and melting . After the fall of the Wall and the peaceful revolution in the GDR , many former employees from the private research institute "Manfred von Ardenne" merged with the newly founded Fraunhofer Institute for Electron Beam and Plasma Technology Dresden, and a pioneering work from 1975 became almost unchanged in 1995 reissued. In the meantime, the use of electron beam technology in the industrial sector has become more widespread, and symposia on the subject are held regularly in the United States of America and East Asia, so that the technology is further developed. Medical technology and aerospace technology are new areas .
significant contributions through:
- Thomas Edison (field emission)
- Heinrich Hertz (further development)
- Ferdinand Braun (cathode tube)
- Heinrich Barkhausen (electron tube characterization)
- Max Dieckmann (TV made from a brown cathode tube)
- Erwin Wilhelm Müller ("first person to see an atom" - invented the electron field microscope)
- Manfred von Ardenne (further development of televisions, microscopes, process engineering applicability)
Use as an information medium
- earlier radio technology
- Picture tube television surface conduction electron emitter display
- Electron microscope , field electron microscope
- Oscillators
- X-ray machines
- Electron beam lithography
Use as an energy source in engineering production processes
The use of electron beam technology in production is a sub-area of production technology , a physics-focused area of general mechanical engineering that partially overlaps with process engineering . Together with other processes, it is used to manufacture goods to satisfy interests within the framework of an economic cycle.
See electron beam material processing
- Evaporation systems electron beam evaporation
- Melting plants electron beam melting
- Processing systems (separating / cutting)
- Welding systems
- Coating plants
- as radiation-chemical (biocidal) treatment of seeds
literature
- Schiller, Heisig, Panzer: electron beam technology; Verlag Technik GmbH Berlin, 1995 (Fraunhofer Institute for Electron Beam and Plasma Technology Dresden)
- Heger, A .: Technology of the radiation chemistry of polymers; Carl Hanser Verlag Munich Vienna, 1990
- Garratt, PG: Radiation Hardening; Curt R. Vincentz Verlag Hannover, 1996
- Helmut Schultz: Electron beam welding (= specialist book series welding technology. Vol. 93). 3rd, completely revised and expanded edition. Verlag DVS - Welding and Related Processes, Düsseldorf 2017, ISBN 978-3-945023-85-3 .
- Klaus-Rainer Schulze: electron beam technologies (= knowledge compact. Vol. 1). DVS Media, Düsseldorf, 2011, ISBN 978-3-87155-225-0 .
- Patent DE102011115913A1 : Joining and separating workpieces with an electron beam in a non-vacuum.