Erogenous zone
An erogenous zone (to Greek ἔρως eros , love 'and -γενής -genes , causing') is a body region, the appropriate stimulation with appropriate desire which a human sexual arousal can cause or increase. The irritation of these areas without corresponding desire or the inappropriate irritation can cause negative feelings up to pain.
Depending on the individual, the receptivity of certain areas varies, it can even change due to emotions. However, the areas of the body that are in all likelihood most susceptible can be clearly identified.
Systematics
The erogenous zones can be divided into two classes: specific and non-specific.
Non-specific erogenous zones
The class of non-specific erogenous zones includes hairy areas of skin and has a normal density of nerve endings and hair follicles. These zones include the sides of the neck and poll, the feet and especially the soles of the feet, the armpits and the sides of the rib cage, the inside of the arms, back and spine, especially in the area of the sacrum , the loins, the abdomen, the buttocks and the Thighs, especially the inner thighs. The feeling of being caressed and the increased expectation of further attention and imminent stimulation of the specific erogenous zones are responsible for the increased arousal.
Specific erogenous zones
The class of specific erogenous zones includes skin and mucous membrane areas that have a high density of nerve endings, and body areas that allow direct stimulation of receptive internal organs in the pelvic area. They usually have a much stronger feeling than the non-specific erogenous zones. Not every one of these zones has to be active or cause a lot of excitement in everyone. In this respect, it is completely wrong and sensational to talk about “super orgasm points”, as various women's and men's magazines often do. There are serious individual differences with regard to the reaction to the stimulation of individual erogenous zones. Typical of specific erogenous zones are the mucocutaneous boundaries , i. H. those zones where the transition from skin to mucous membrane takes place, as the nerve density is particularly high here.
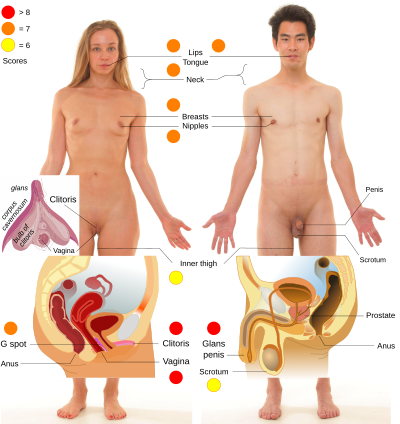
The specific erogenous zones in men and women include the area of the eyes , the auricles , nose and mouth ( lips , tongue , corners of the mouth and the entire oral cavity ), eyebrows , inside of the nostrils, the hairline in the forehead area , the area from the Fingertips to the palms of the hands, armpits , the area of the perineum and anus ; rather in women, less often in men , the breast hillocks , areolas and nipples .
With the man
In men, the penis (especially the mucocutaneous border of the foreskin - called the furrowed band , the inner foreskin , the foreskin ligament, the lower edge of the glans and the glans itself) and scrotum itself .
With the woman
In women, the mons pubis with the large and small labia , the clitoris (called "C point" by some modern authors), in the vaginal vestibule in particular the area of the urethral opening ( called " U point " by some modern authors ) of the sheath , particularly in the anterior vaginal wall of the region in the vicinity of the upper urethra, G-spot or "point G" mentioned, the range in the vaginal vault, near the cervix - more recently, " A-point referred to as" - and of the cervix (portio) .
Erogenous Zones and Sexual Practice
Not only the special erogenous zones, but the entire surface of the human body (e.g. by caressing) can have an erogenous effect. Due to the individuality of every single person, there are hardly any universally applicable instructions for use for sexual practice, but only certain basic rules. There are no erogenous zones that inevitably lead to deep sexual satisfaction at all times, not even G-spot , A-spot , C-spot or U-spot .
Most sexual practices involve irritation of the erogenous zones, e.g. B. kissing , intercourse , petting or masturbation .
Alternative opinions
The erogenous zones of men and women are largely identical.
The vaginal mucosa itself has relatively few nerve endings. The sexual stimulation during intercourse is therefore primarily based on the irritation of the clitoris. The effect of vaginal balls ( Rin-no-tama ), for example, comes from the awareness of wearing them and from the vibrations in the cervix.
According to Sigmund Freud's drive theory , people already have a sexual drive from infancy and satisfy it by stimulating their erogenous zones, initially the oral (sucking, sucking), later also the anal and genital zones (see also: Infantile sexuality according to Freud ) . The drive concept is now only used sporadically in scientific literature. Freud's drive theory is still very controversial today. Within psychoanalysis , object relationship theory has gained in importance compared to drive theory, which ascribes real and fantasized interpersonal relationships an independent meaning that goes beyond the drive object .
Web links
Individual evidence
- ↑ erogenous. duden.de, accessed on November 30, 2013 .
- ^ Turnbull OH, Lovett VE, Chaldecott J., Lucas MD: Reports of intimate touch: Erogenous zones and somatosensory cortical organization. Cortex, 2013 from S. Wunsch: Role and importance of reinforcement processes in the learning of the reproductive behavior in humans. Dissertation, EPHE-Sorbonne, Paris 2007