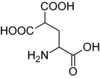Gamma glutamyl carboxylase
| Gamma glutamyl carboxylase | ||
|---|---|---|
| Properties of human protein | ||
| Mass / length primary structure | 758 amino acids | |
| Secondary to quaternary structure | Monomer; multipass membrane protein | |
| Cofactor | Vitamin K | |
| Identifier | ||
| Gene name | GGCX | |
| External IDs | ||
| Enzyme classification | ||
| EC, category | 6.4.-.- , ligase | |
| Response type | Carboxylation | |
| Substrate | X-Glu-Y (protein) | |
| Products | X-Gla-Y (calcium-binding protein) | |
The γ-Glutamylcarboxylase (or short GGCX ) is an enzyme that using the cofactor vitamin K special glutamyl residues of various proteins in the gamma position carboxylated , activating these proteins. These include factors that promote coagulation ( II , VII , IX , X ) and anticoagulant factors such as proteins C and S but also proteins such as osteocalcin and matrix Gla protein or ligands for receptor tyrosine kinases such as Gas6 . This carboxylation is required for the protein functions, for example the coagulation factors, because it allows them to bind calcium and to bind to phospholipids .
GGCX is a membrane enzyme of the rough endoplasmic reticulum . GGCX contains 758 amino acids and is encoded in humans in the gene locus p12 on chromosome 2 . The gene contains 15 exons .
The enzyme catalyzes the following reaction (however, there are no free amino acids, but these are incorporated into a protein):
Clinical significance
A deficiency can lead to the rare clinical picture of hereditary combined deficiency of vitamin K-dependent coagulation factors .
literature
- SM Wu, WF Cheung, D. Frazier, DW Stafford: Cloning and expression of the cDNA for human gamma-glutamyl carboxylase. In: Science . 254 (5038), December 1991, pp. 1634-1636. doi: 10.1126 / science.1749935 . PMID 1749935 .
- B. Brenner, S. Tavori, A. Zivelin, CB Keller, JW Suttie, I. Tatarsky, U. Seligsohn: Hereditary deficiency of all vitamin K-dependent procoagulants and anticoagulants. In: British Journal of Hematology . 75 (4), Aug 1990, pp. 537-542. doi: 10.1111 / j.1365-2141.1990.tb07795.x . PMID 2145029 .
- JW Suttie: Vitamin K-dependent carboxylase. In: Annual Review of Biochemistry . 54, 1985, pp. 459-477. doi: 10.1146 / annurev.bi.54.070185.002331 . PMID 3896125 .
- SR Presnell, DW Stafford: The vitamin K-dependent carboxylase. In: Thrombosis and Haemostasis . 87 (6), 2002, pp. 937-946. PMID 12083499 .
- PJ Silva, MJ Ramos: Reaction mechanism of the vitamin K-dependent glutamate carboxylase: a computational study. In: J Phys Chem B. 111 (44), 2007, pp. 12883-12887. doi: 10.1021 / jp0738208 . PMID 17935315 .
- OM Vanakker, L. Martin, D. Gheduzzi, BP Leroy, BL Loeys, VI Guerci, D. Matthys, SF Terry, PJ Coucke, I. Pasquali-Ronchetti, A. De Paepe: Pseudoxanthoma elasticum-like phenotype with cutis laxa and multiple coagulation factor deficiency represents a separate genetic entity. In: Journal of Investigative Dermatology . 127 (3), March 2007, pp. 581-587. doi: 10.1038 / sj.jid.5700610 . PMID 17110937 .