Receptor tyrosine kinases
| Receptor tyrosine kinases | ||
|---|---|---|
|
||
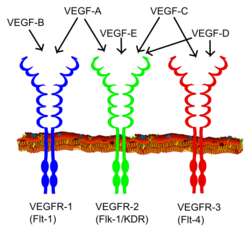
| Scheme drawing of VEGF receptors | ||
| Enzyme classification | ||
| EC, category | 2.7.10.1 , protein kinase | |
| Substrate | ATP + protein L-tyrosine | |
| Products | ADP + protein L-tyrosine phosphate | |
Receptor tyrosine kinases ( RYKs , formerly also RTKs ) are receptors bound to the cell membrane , whose intracellular domain carries an enzyme group , the tyrosine kinase , which enables the phosphorylation of tyrosine residues of proteins. You are u. a. involved in cell growth . The classification of RTKs into three different types is based primarily on the extracellular domains, i.e. H. the areas of the receptor that are outside the cell. In all three types, the N terminus is on the outside of the cell, while the C terminus is inside the cell.
Types of receptor tyrosine kinases:
- EGF receptor type: cysteine- rich extracellular domain, single chain.
- Insulin receptor type: two α and two β chains, the extracellular parts of which are linked by disulfide bridges .
- NGF receptor type: antibody- like extracellular domain; the (intracellular) kinase domain can be interrupted by insertions.
Examples of hormones that interact with receptor tyrosine kinases are insulin , insulin-like growth factor I ( insulin-like growth factor , IGF I), platelet- derived growth factor (PDGF), epidermal growth factor ( Epidermal Growth Factor , EGF) or the fibroblast growth factor ( FGF ).
Various vitamin K -dependent proteins have been identified that act as ligands for receptor tyrosine kinases, such as Protein S or Gas6 .
See also: growth factor , kinase
literature
- Bruce Alberts , Alexander Johnson, Peter Walter , Julian Lewis, Martin Raff , Keith Roberts: Molecular Biology of the Cell. 5th edition. Garland Science, New York NY et al. 2008, ISBN 978-0-8153-4106-2 .
- Jeremy M. Berg, John L. Tymoczko, Lubert Stryer : Biochemistry. 6 edition. Spectrum - Akademischer Verlag, Heidelberg 2007, ISBN 978-3-8274-1800-5 .
- Donald Voet, Judith G. Voet: Biochemistry. 3. Edition. Hoboken, NJ et al. 2004, ISBN 0-471-19350-X .