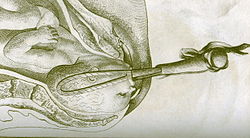
Face position
The face position is an obstetric postural abnormality of the child in the womb. The physiological flexion of the child's head has not taken place and has turned into an extension, the face has taken the lead. One also speaks of an extension or deflection position. If the head is already in a stretched position in the pelvic entrance , there is, according to an exact definition, an adjustment anomaly . In the subsequent course of labor, however, it is referred to as a face position.
frequency
The frequency of the face position is given as 1: 500 births.
root cause
Child causes can be an unfavorable head shape, child malformations (e.g. anencephaly ) or a child with a low birth weight.
The maternal cause can be a flat or male pelvis . In multiparous women, a very flabby abdominal wall can be the cause, as this can cause an anteflexion (bending forward) of the uterus, which also shifts the child's axis forward and the child's rump can come very far forward.
The reason can also be a rupture of the bladder when there is a very large amount of amniotic fluid (polyhydramnios), the head can become stretched as a result of the amniotic fluid flowing out in the surge.
Classification
Mentoanterior face position : The child's back lies behind. The effective obstetric head circumference is 34–35 cm. The point where the head emerges is the neck in the larynx area ( hypomochlion ). A spontaneous delivery is basically possible.
Mentoposterior face position : The child's back is in front. The effective obstetric head circumference is 34–36 cm. The point where the head emerges is the area of the large fontanel . Further stretching is not possible, the birth must be ended by caesarean section . The mentoposterior face position is very rare.
Diagnosis
During the external examination, the heart sounds can be heard very clearly at the level of the navel or a little below. With the third and fourth Leopold manipulations, there is a deep incision above the child's head, under certain circumstances the head can be felt as a hard ball.
The chin should be palpated during the internal examination. If only the mouth is palpable, the forehead is present. The internal examination should be carried out very carefully and gently if a posture anomaly is suspected (risk of injury to the child). In terms of differential diagnosis, breeches should be considered. If in doubt, the findings should be confirmed by ultrasound .
Course of birth
With the face position, the head can already be in maximum extension at the pelvic entrance. From the other Deflexionslagen ( frontal position , front main location , crown ply ) birth can give a face position in the course. The back of the child's head comes closer and closer to the spine, up to the maximum possible extension. The face line (corresponds to the arrow seam , an imaginary line from the forehead over the nose, mouth and chin) rotates over the opposite diagonal diameter. The head reaches maximum extension on the pelvic floor at the latest . The chin, mouth and nose appear one after the other under the symphysis, followed by the forehead, vertex and occiput (bending is now possible again).
Complications
The opening and expulsion phase is severely delayed. Since the head can hardly configure itself, it only steps deeper slowly. The perineum is stretched very much, which can lead to maternal injuries. Since the face does not seal properly, an umbilical cord prolapse can occur. Cerebral haemorrhage , tentorial tears and a lack of oxygen can occur in the child . In any case, the child has a very pronounced facial edema , but this subsides after 2-3 days.
Therapy and specifics
No rind electrode may be placed. If the bladder ruptures, a vaginal examination must be carried out immediately to rule out an umbilical cord prolapse. In the case of a vaginal-operative delivery, a forceps must be performed; a suction cup is contraindicated. If possible, the passage of the head can be supported by the Ritgen hind dam handle . Depending on the child's and maternal condition, the indication for a caesarean section should be generously given.
literature
- Mändle, Opitz, Kreuter: The midwifery textbook of practical obstetrics. ISBN 3-7945-1765-2