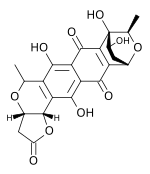
Granaticin
| Structural formula | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|||||||||||||
| General | |||||||||||||
| Surname | Granaticin | ||||||||||||
| other names |
|
||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 22 H 20 O 10 | ||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | |||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||
| properties | |||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 444.39 g mol −1 | ||||||||||||
| Melting point | |||||||||||||
| safety instructions | |||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||
| Toxicological data | |||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | |||||||||||||
Granaticin is an antibiotic that is produced by a group of Streptomycetes e.g. B. Streptomyces olivaceus is formed. Since it is too expensive to manufacture and has severe side effects, it is not used as a medicinal substance .
Chemical properties
Granaticin comes in different varieties. It consists of six rings of aromatic or aliphatic character with alcoholic and phenolic hydroxyl groups as well as keto groups . It has an intense color that depends on the pH value . At an acidic pH value, it absorbs light most strongly in the range of 300 and 500 nm and is colored red. At a basic pH value, it absorbs light most strongly in the range of 300 and 600 nm and is colored blue. The pure form forms red cubic crystals, whose similarities with garnet led to the formation of the name.
Mode of action
Granaticin works against gram-positive bacteria by inhibiting the leucine aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase . This enzyme connects leucine with the corresponding tRNA and enables the incorporation of leucine into bacterial proteins . Since it is a reversible competitive inhibition, the effect can be weakened by a high leucine concentration.
Ecological importance
Granaticin, like many other antibiotics, is believed to be made to harm competitors. This is how other soil bacteria react, such as B. Bacillus subtilis very sensitive to granaticin. The formation is often temporally related to the spore formation and is likely to be related to a shortage of nutrients.
Individual evidence
- ^ The Merck Index : An Encyclopedia of Chemicals, Drugs, and Biologicals , 14th Edition (Merck & Co., Inc.), Whitehouse Station, NJ, USA, 2006; P. 782, ISBN 978-0-911910-00-1 .
- ↑ a b Entry on Granaticine. In: Römpp Online . Georg Thieme Verlag, accessed on June 8, 2014.
- ↑ This substance has either not yet been classified with regard to its hazardousness or a reliable and citable source has not yet been found.
- ↑ Jürgen Falbe, Manfred Regitz: Römpp Lexikon Chemie, Volume 2, 10th edition, 1996-1999: Volume 2: Cm - G . Georg Thieme Verlag, 2014, p. 1598 ( limited preview in Google Book search).
literature
- P. Heinstein: Mechanism of action of granaticin: Inhibition of ribosomal RNA maturation and cell cycle specificity. In: Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences. Feb. 1982, pp. 197-200, doi : 10.1002 / jps.2600710215 .