Greek juniper
| Greek juniper | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|

Greek juniper near Antalya , Turkey |
||||||||||||
| Systematics | ||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||
| Scientific name | ||||||||||||
| Juniperus excelsa | ||||||||||||
| M.Bieb |
The Greek juniper ( Juniperus excelsa ) is a plant from the genus of juniper ( Juniperus ) in the family of cypress plants (Cupressaceae).
description
Vegetative characteristics
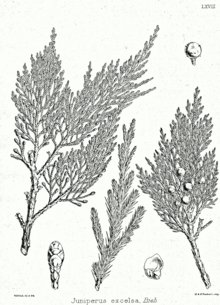
The Greek juniper grows as an evergreen tree that reaches heights of up to 20 meters or as an upright to prostrate shrub . The treetop is conical in young trees and later develops into a wide and open habit . The light brown bark separates from the trunk in narrow strips. The stem-round and thin branches reach a diameter of only 0.6 to 0.8 millimeters.
The needle-shaped leaves of juvenile trees are 5 to 6 millimeters long. The scale-like leaves of adult trees are 0.6 to 1.1 mm long and 0.4 to 0.8 mm wide at the end branches. They show an egg-shaped-rhombic shape, are firmly pressed against the branches, pointed and have a central egg-shaped or linear resin gland on the back of the leaf . The leaf margins are entire .
Generative characteristics
The Greek juniper is single- sexed ( monoecious ) as well as dioecious ( dioecious ). The spherical seed cones have a diameter of 8 millimeters. They ripen in the second year, are spherical, slightly frosted and, when ripe, are dark purple-brown. A cone contains four to six seeds.
Occurrence
The distribution area extends from the eastern Mediterranean area ( Albania , South Bulgaria , Macedonia , North Greece , Anatolia , Cyprus , Lebanon ) over the Black Sea region ( Crimea peninsula , Caucasus region ) to the Elburs Mountains in the south of the Caspian Sea. Its elevation ranges from 100 to 1000 meters in the Crimea and up to 2300 meters in the Caucasus and Turkey.
Its populations form the tree line in several mountains . Its occurrence is determined by annual precipitation between 500 and 1000 mm. It occurs mainly on stony rock slopes on calcareous or lime-poor subsoil and occurs there in pure stands, mixed with other conifers such as the stinking juniper or in secondary stands with shrub-shaped oaks . Further to the east, the species is being replaced by the closely related Juniperus polycarpos , which is adapted to even more extreme climatic conditions.
Systematics
The Greek juniper ( Juniperus excelsa M.Bieb. ) Is part of the cypress family (Cupressaceae) within the genus Juniperus in the Sabina section . He was accompanied by Marshal von Bieberstein in 1798 in Tableau des provinces situées sur la côte occidentale de la mer Caspienne entre les fleuves Terek et Kour first described . The following synonyms are listed among others: Juniperus lycia Pall. , Juniperus isophyllos K. Koch , Juniperus olivieri Carrière , Juniperus aegaea Griseb. and Juniperus taurica (Pall.) Lipsky (non Lindl. )
The subspecies Juniperus excelsa subsp. polycarpos (K. Koch) Takht. Juniper seen here is listed as Juniperus polycarpos K.Koch .
Hazards and protective measures
The Greek juniper is common in parts of its range and therefore does not appear to be endangered. The IUCN accordingly lists it in its Red List of Endangered Species with “Least Concern”.
With the Fauna-Flora-Habitat Directive No. 92/43 / EEC in the updated version of January 1, 2007 of the European Union (FFH-RL) Appendix 1, the Bulgarian, Greek and Cypriot stocks are required to designate protected areas to which juniper species belong , protected.
swell
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c Christopher J. Earle: Juniperus excelsa. In: The Gymnosperm Database. Retrieved December 1, 2010 .
- ^ A b c Robert P. Adams: Junipers of the World: The genus Juniperus . 2nd Edition. Trafford, Victoria 2008, ISBN 978-1-4251-6879-7 , pp. 85 and 182-183 .
- ^ Friedrich August Marschall von Bieberstein: Tableau des provinces situées sur la côte occidentale de la mer Caspienne entre les fleuves Terek et Kour . St. Petersburg, 1798, p. 120 ( preview in Google book search)
- ↑ Knud Ib Christensen: Juniperus in Arne Strid, Kit Tan (ed.): Flora Hellenica. Volume One (Gymnospermae to Caryophyllaceae) . Koeltz Scientific Books, Königstein 1997, ISBN 3-87429-391-2 , p. 14 .
- ↑ Juniperus excelsa in the IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2010.4. Listed by: Conifer Specialist Group, 1998. Retrieved December 1, 2010.
- ↑ Directive 92/43 / EEC of the Council of May 21, 1992 on the conservation of natural habitats and of wild animals and plants in the consolidated version of January 1, 2007 , accessed on December 1, 2010 , p. 19.
Web links
- RPAdams: The Juniperus of the World / Taxa of Juniperus. Retrieved December 1, 2010 .
- Christopher J. Earle: Juniperus excelsa. In: The Gymnosperm Database. Retrieved December 1, 2010 .
- Germplasm Resources Information Network (GRIN): Taxon: Juniperus excelsa M.Bieb. In: GRIN Taxonomy for Plants. United States Department of Agriculture Agricultural Research Service, accessed December 1, 2010 .