Guanosine diphosphate
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
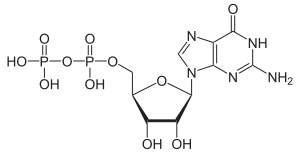
|
||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Guanosine diphosphate | |||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
|||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 10 H 15 N 5 O 11 P 2 | |||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 443.2 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
|||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||||||||
Guanosine diphosphate ( GDP ) is the diphosphate of the nucleoside guanosine . It plays an important role as a cellular energy carrier and breakdown product of guanosine triphosphate . Guanosine diphosphate is also involved as a cofactor of G proteins in the transmission of external stimuli into the cell interior ( signal transduction ).
GDP is produced in the cell by dephosphorylation of guanosine triphosphate (GTP) by GTPases .
See also
Individual evidence
- ↑ This substance has either not yet been classified with regard to its hazardousness or a reliable and citable source has not yet been found.
- ^ Gerhard founder, Otto Benkert: Handbook of psychopharmacotherapy . Springer-Verlag, 2011, ISBN 978-3-642-19844-1 , p. 64 ( limited preview in Google Book search).