Hebrew roller screw
| Hebrew roller | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|

Voluta ebraea in situ |
||||||||||||
| Systematics | ||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||
| Scientific name | ||||||||||||
| Voluta ebraea | ||||||||||||
| Linnaeus , 1758 |
The Hebrew roller or Hebrew roller snail ( Voluta ebraea ) is a snail from the family of roller snails (genus Voluta ) that is common on the coast of Brazil . It feeds on snails and clams .
features
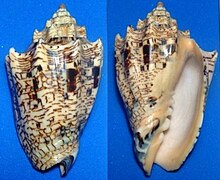
The egg-shaped, thick, axially ribbed snail shell of Voluta ebraea , which in adult snails reaches a length of about 10 to 15 cm, exceptionally also more than 20 cm, has a conical, knotty , tuberous thread with tuberous circumferences and a columella with 5 folds, from which the lower ones are greatest. The whorls are crowned with large bumps at the top. The pale yellow-brown surface of the case is drawn with spiraling brown-red, wavy lines that stand in crowded bands.
The horny operculum is pointed ovoid and covers part of the case mouth.
Like the shell, the snail is whitish and drawn with a similar pattern of dark brown lines. She has a large, sturdy foot and a long siphon .
distribution
The Hebrew roller lives in the western Atlantic Ocean on the coast of Brazil . It is isolated from the Caribbean note snail by the freshwater barrier at the mouth of the Amazon.
Habitat and way of life
The Hebrew roller lives in the intertidal zone and up to 40 m depth, mainly on sandy ground, but it can also be found on rocks, on sand between algae and on gravel. It is absent in water with insufficient salt content.
Voluta ebraea eats mussels and snails . Hebrew slugs observed on reefs off Cabo Branco ( João Pessoa , Paraíba ) are diurnal and eat cockles ( Trachycardium muricatum ), apparently detecting their prey through chemical stimuli. When approaching the clam, the snail lifts the leading edge of its foot and buries it under it.
Life cycle
Like other new snails, Voluta ebraea is segregated. The male mates with the female with his penis . The female attaches her translucent, hemispherical egg capsules, which have a diameter of about 18 mm (15 to 30 mm), with the flat side individually to a solid substrate, according to observations in seagrass meadows on the beach of Paracurú ( Ceará ) on the green alga Udotea occidentalis . One egg capsule contains around 5 eggs in a protein-rich nutrient medium. The Veliger stage, during which the embryo with its velum creates a constant flow of fluid and thereby absorbs nutrient fluid, is passed through entirely within the egg capsule. 2 to 5 (on average 3) snails develop per capsule. After several weeks, young, ready-made snails hatch through an opening in the middle of the capsule, which is connected to the rim by a seam. Measurements in Paracurú have shown that their shells are around 8 mm long and have around 2 ¼ turns. Due to the lack of a pelagic Veliger stage, the snail has a limited range.
Enemies
Despite its thick shell, Voluta ebraea has enemies. The most important predators are octopuses , including the common octopus .
Human use and exposure
Voluta ebraea is collected for its case, which is sold as jewelry. In addition, the meat is eaten. The species is classified as endangered due to overfishing . Due to its relatively small number of offspring and the lack of a pelagic Veliger stage, it can only repopulate lost habitats with difficulty. A key to the conservation of the species is seen in the protection of the clutch.
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e Thelma Lúcia Pereira Dias (2009): First field study of the Brazilian endemic marine gastropod Voluta ebraea (Mollusca: Volutidae) . Marine Biodiversity Records 2, e10, doi : 10.1017 / S1755267208000109 .
- ^ C. Brüggemann (1838): The natural history in faithful illustrations and with a detailed description of the same. Eduard Eisenach publisher, Leipzig 1838. Die Weichthiere, p. 61. The Hebrew or mild music or note snail. Voluta ebraea Linn.
- ↑ Carolus Linnaeus : Systema Naturae. 10th ed., Lars Salvius: Stockholm 1758, p. 729, 287. Voluta , p. 733, 372. Voluta ebraea. V. testa fusiformi, anfractibus spinis subacutis, columella plicis quinque validioribus tribusque obsoletis. Habitat in O. Asiatico. (The last sentence was proven to be false due to a sending of snail shells to Wilhelm Kobelt : On the marine fauna of Brazil . News sheet of the German Malakozoological Society, No. 8, August 1874, p. 57).
- ↑ Peter L. Perchade (1976): Voluta musica Linnaeus 1758 (Mollusca). A local marine mollusc of interest to geologists as a fine example of the evolutionary process ( Memento of the original from March 18, 2013 in the Internet Archive ) Info: The archive link was inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice. . Newsletter 1, The Geological Society Of Trinidad & Tobago.
- ↑ a b Helena Matthews-Cascon, Cristina Rocha-Barreira, Pablo E. Penchaszadeh & Gregorio Bigatti (2010): Description of egg capsules of Voluta ebraea Vinnaeus, 1758 (Gastropoda: Neogastropoda) ( Memento of the original from October 30, 2012 on the Internet Archive ) Info: The archive link was inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice. (PDF; 614 kB) . Comunicaciones de la Sociedad Malacológica del Uruguay 9 (93), pp. 237-244.
- ↑ Helena Matthews-Cascon, Cristina Rocha-Barreira, Reynaldo Amorim Marinho, Lorena Galletti de Almeida, Carlos Augusto Oliveira de Meirelles (2009): Mollusks Found Inside Octopus (Mollusca, Cephalopoda) Pots in the State of Ceará, Northeast Brazil (PDF; 2.0 MB) . The Open Marine Biology Journal (2009) 3, pp. 1-5. doi : 10.2174 / 1874450800903010001