Heino Falcke (astronomer)
Heino Falcke (* 1966 in Cologne ) is a German radio astronomer . He is a professor at Radboud University Nijmegen .
Life
Falcke is the eldest of two sons of the doctor Sigurd Falcke (* 1940 in Königsberg ) and his wife Erika. After graduating from high school in Frechen , he studied physics at the universities of Cologne and Bonn , which he completed in 1992. In 1994 he received his doctorate summa cum laude from the University of Bonn ( starving holes and active nuclei: the central machine in galactic centers ). He worked as a scientist at the Max Planck Institute for Radio Astronomy (MPIfR). He then worked at their optical interferometer group and as a post-doctoral student at the University of Maryland . From 1999 he was a permanent scientist at the MPIfR and visiting professor at the Steward Observatory in Tucson . In 2001 he received his habilitation and was a private lecturer at the University of Bonn, and in 2002 he was assistant professor and in 2007 he was professor at Radboud University Nijmegen . Since 2003 he has been a senior scientist in the Low Frequency Array Project (LOFAR).
He is also working with the European Space Agency (ESA), the National Center for Space Science of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, and the Department of Science and Technology of Radio Astronomy of the Shanghai Astronomical Observatory on projects to extend the LOFAR project to the moon . He is interested in the SETI project and deals with radio waves from showers of cosmic rays, black holes (for example the one in the center of the Milky Way in the Sagittarius A * area ), active galaxy nuclei , Seyfert galaxies and LINER galaxies .
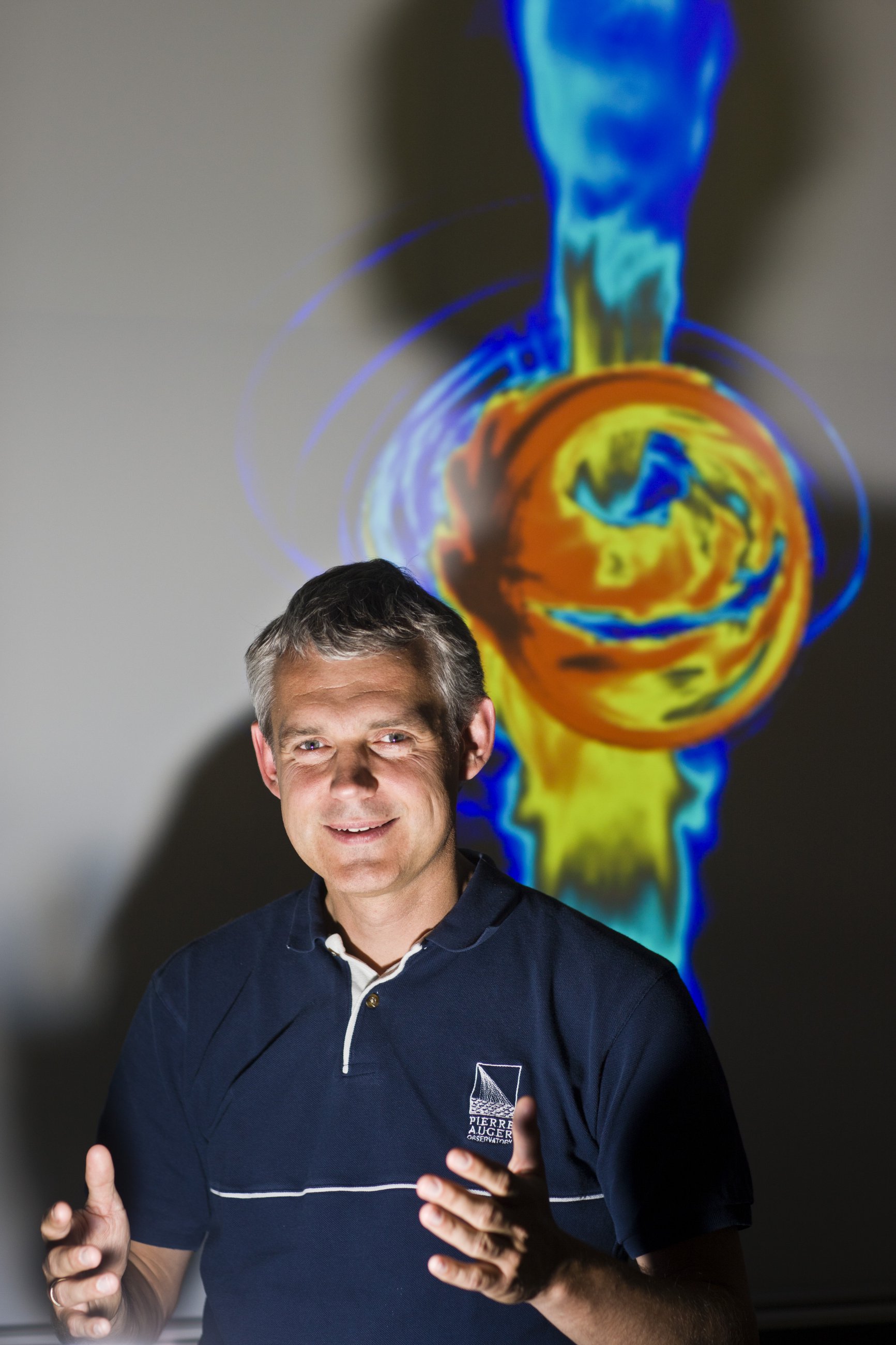
In 2000, together with Eric Agol and Fulvio Melia , he proposed the possibility of observing the event horizon with interconnected radio telescopes (VLBI at submillimeter wavelengths), which is implemented in the Event Horizon Telescope . This was successful in April 2019 with the image of the central black hole in M 87 .
2013 he developed with Luciano Rezzolla ( Max Planck Institute for Gravitational Physics in Potsdam) a theory to explain the rapids radio flashes ( fast radio burst , FRB), which in 2007 first discovered by Duncan Lorimer and David Narkevic. They only lasted a few milliseconds and did not repeat themselves. Their source was also likely billions of light-years away, much farther than the most distant observable pulsars. According to Falcke and Rezzolla, they arise when, after a supernova, the collapsed star should actually form a black hole in terms of mass, but is initially prevented from collapsing due to the high rotational speed. The collapse to the black hole only takes place after some time under radiation of the magnetic field of the rotating neutron star, which leads to the radio burst. They named their model Blitzar .
Falcke is a member of the Dutch National Institute for Nuclear and Particle Physics ( NIKHEF ) and a visiting scientist at the Max Planck Institute for Radio Astronomy .
He lives in Frechen , is married and has three children. As a predicant of the Evangelical Church in the Rhineland , he also holds services in the Evangelical Church in Frechen .
Awards and honors
In 2000 he received the Ludwig Biermann Prize . In 2006 he received the Academy Award from the Berlin-Brandenburg Academy of Sciences . and in 2008 an Advanced Grant from the European Research Council . In 2011 he won the Spinoza Prize , the highest Dutch science award . At the end of 2013, together with three colleagues from his research association, he received an EU Synergy Grant of € 14 million, the most highly endowed and most sought-after funding awarded by the European Research Council , for the construction of a virtual camera for the first visualization of a black hole at Sagittarius A.
He has been a full member of the Academia Europaea since 2013 . In 2016 he was made a Knight of the Order of the Dutch Lion .
On April 6, 2019, an asteroid was named after him: (12654) Heinofalcke .
Web links
- Homepage
- Literature by and about Heino Falcke in the catalog of the German National Library
- Literature by and about Heino Falcke in the bibliographic database WorldCat
- Jörn Schumacher: When the invisible becomes visible. (pdf, 5.9 MB) In: Pro Medienmagazin 1/2018. February 6, 2018, pp. 32–34 .
- Ralf Nestler: Interview with Heino Falcke: “We make weather models for black holes”. In: Golem.de . April 25, 2019 .
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c German scientist Heino Falcke receives the highest science award in the Netherlands ( Memento of the original from September 24, 2015 in the Internet Archive ) Info: The archive link has been inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice. ru.nl, accessed on December 29, 2012.
- ^ Heino Falcke, Hong Xiaoyu et al .: DSL: Discovering the Sky at the Longest Wavelengths. In: astron.nl. Retrieved July 30, 2019 .
- ↑ Low ionization nuclear emission line region , areas of low ionization in the center of galaxies, next to an intermediate position between active and inactive galaxies, where the cause of the ionization could be a black hole or a region of high star formation.
- ^ Falcke, Melia, Agol: Viewing the Shadow of the Black Hole at the Galactic Center , Astroph. J. Letters, vol. 528, 2000, p. 13, abstract
- ↑ Govert Schilling, Mystery radio bursts blamed on black hole 'blitzars' , New Scientist, July 4, 2013
- ↑ Falcke, Rezzola, Fast radio bursts: the last sign of supramassive neutron stars , Astronomy and Astrophysics, Volume 562, 2013, A 137
- ↑ Falcke, Rezzolla, Blitzars: Fast Radio Bursts from Supramassive Rotating Neutron Stars
- ↑ Homepage Heino Falcke , see "Private Stuff", at the bottom (accessed on September 15, 2017)
- ↑ Divine service plan of the Protestant parish Frechen
- ↑ MPI communication of December 17, 2013 (accessed January 23, 2014)
- ↑ Directory of members: Heino Falcke. Academia Europaea, accessed October 20, 2017 .
- ↑ Lintjesregen in Nijmegen Persbericht Gemeente Nijmegen dd 26 April 2016
| personal data | |
|---|---|
| SURNAME | Falcke, Heino |
| BRIEF DESCRIPTION | German astronomer |
| DATE OF BIRTH | 1966 |
| PLACE OF BIRTH | Cologne |