Imidic acid ester
Imidate ester (alternative names: imidates , Carboximidate , imide ester , imido ester , imino ester , imino ether ) are a group of chemical compounds , the functional group R 1 -C (= NH) - (OR 2 included). These compounds are derived from the imidic acids , a tautomeric form of the carboxamides . The imidic acid esters have a basic reaction and form salts with acids .
presentation
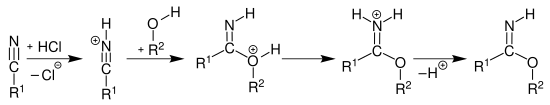
The imidic acid esters can be prepared from nitriles by adding an alcohol in the presence of anhydrous hydrogen chloride and subsequent deprotonation of the hydrochloride formed as an intermediate with a weak base - for example sodium hydrogen carbonate - ( Pinner reaction ):
Alternative ways of preparing imidic esters are:
- the O - alkylation of amides with oxonium - tetrafluoroborate salts.
- the reaction of monohydric phenols with nitriles under the conditions of the Houben-Hoesch reaction .
- N -substituted imidate ester is obtained by reacting amino-aromatic or amino heteroaromatic compounds with Orthocarbonsäureestern .
- Cyclic imidic esters - for example 2-oxazoline (4,5-dihydro-1,3-oxazole) - are obtained by reacting amino alcohols with carboxylic acids or carboxylic acid chlorides with elimination of water (example: 2-ethyl-2-oxazoline ).
properties
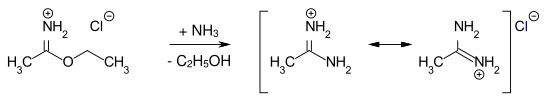
Imidic acid esters are relatively stable to water under neutral conditions. When arylimidic esters are heated, the N , N -diarylamides are formed ( Chapman rearrangement ). Amidines are obtained by reacting imidic ester hydrochlorides with anhydrous ammonia . Example:
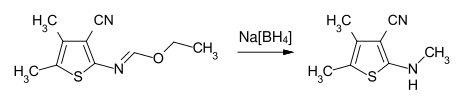
With metal hydrides or complex hydrides such as sodium borohydride , N -substituted imidic esters can be reduced to secondary or tertiary amines.
Example:
literature
- Stanley Sandler and Wolf Karo: Organic Functional Group Preparations . 2nd Edition. Academic Press, San Diego 1989, pp. 314-350 .
- H. Pielartzik, B. Irmisch-Pielartzik, Theophil Eicher: Carboxylic acid ester-imides, hydroximides, hydroximides, -hydrazonides and 1-alkoxy-1-diazo-alkanes . In: Houben-Weyl . Methods of Organic Chemistry. 4th edition. E 5. Georg Thieme Verlag, Stuttgart, New York 1985, ISBN 978-3-13-217504-4 , pp. 812 ff . ( limited preview in Google Book search).
Individual evidence
- ^ A b Hans Beyer, Wolfgang Walter: Textbook of organic chemistry . 18th edition. S. Hirzel Verlag, Stuttgart 1978, ISBN 3-7776-0342-2 , p. 230 .
- ↑ Michael B. Smith, Jerry March: March's Advanced Organic Chemistry . Reactions, Mechanisms and Structure. 6th edition. John Wiley & Sons, Hoboken, New Jersey 2007, ISBN 978-0-471-72091-1 , pp. 1275 (English, limited preview in Google Book search).
- ↑ Entry on imidic acids. In: Römpp Online . Georg Thieme Verlag, accessed on February 4, 2019.
- ↑ Hartwig Perst: Oxonium Ions in Organic Chemistry . Verlag Chemie, 1971, ISBN 3-527-25348-3 , pp. 128-137 (English).
- ↑ Michael B. Smith, Jerry March: March's Advanced Organic Chemistry . Reactions, Mechanisms and Structure. 6th edition. John Wiley & Sons, Hoboken, New Jersey 2007, ISBN 978-0-471-72091-1 , pp. 732 (English, limited preview in Google Book search).
- ↑ Michael B. Smith, Jerry March: March's Advanced Organic Chemistry . Reactions, Mechanisms and Structure. 6th edition. John Wiley & Sons, Hoboken, New Jersey 2007, ISBN 978-0-471-72091-1 , pp. 1697 (English, limited preview in Google Book Search).
- ^ Andor Hajós: Reduction with metal hydrides or complex hydrides . In: Houben-Weyl . Methods of organic chemistry. 4th edition. IV / 1d Reduction Part II. Georg Thieme Verlag, Stuttgart, New York 1981, ISBN 978-3-13-217504-4 , p. 812 ff . ( limited preview in Google Book search).