Orient
| Structural formula | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
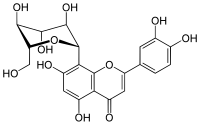
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| General | |||||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Orient | ||||||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 21 H 20 O 11 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
white to yellow odorless solid |
||||||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| properties | |||||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 448.383 g mol −1 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
265-267 ° C |
||||||||||||||||||
| solubility |
|
||||||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | |||||||||||||||||||
Orientin is a naturally occurring, glycated flavonoid , more precisely a glycated flavone . As an isolated substance, it is in the form of a yellow solid.
Occurrence
Orientin is found in many different plants, including the passion flower , rooibos , some types of bamboo and the Japanese iris .
Biological importance
Orientin has an antioxidant effect . In animal studies also it acts anti-inflammatory .
Isomers
The regioisomer isoorientin is also present as a natural product in various plants, including bamboo and passion fruit .
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c Carl Roth: Safety data sheet Orientin (PDF; 40 kB)
- ^ A b V. C. da Silva, PT de Sousa Jr., EL Dall'oglio, GE Matiz, MG de Carvalho: Anti-inflammatory activities of flavonoids from Luxemburgia octandra flowers . In: Chemistry of Natural Compounds . tape 46 , no. 6 , 2011, p. 961-963 , doi : 10.1007 / s10600-011-9796-5 .
- ↑ a b c N. I. Pryakhina, KF Blinova: Luteolin C-glycosides from Iris ensata . In: Chemistry of Natural Compounds . tape 20 , no. 1 , 1084, ISSN 0009-3130 , p. 107 .
- ↑ a b c d Orientin data sheet at Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on December 23, 2019 ( PDF ).
- ↑ ER Pastene, G. Bocaz, I. Peric, M. Montes, V. Silva, E. Riffo: Separation by capillary electrophoresis of C-glycosylflavonoids in Passiflora sp. extracts . In: Boletín de la Sociedad Chilena de Química . tape 45 , no. 3 , 2000, pp. 461-467 , doi : 10.4067 / S0366-16442000000300017 .
- ↑ Astrid von Gadow, Elizabeth Joubert, Chris F. Hansmann: Comparison of the Antioxidant Activity of Aspalathin with That of Other Plant Phenols of Rooibos Tea (Aspalathus linearis), α-Tocopherol, BHT, and BHA . In: Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry . tape 45 , no. 3 , 1997, p. 632-638 , doi : 10.1021 / jf960281n .
- ↑ Yu Zhanga, Jingjing Jiaoa, Chengmei Liub, Xiaoqin Wua, Ying Zhang: Isolation and purification of four flavone C-glycosides from antioxidant of bamboo leaves by macroporous resin column chromatography and preparative high-performance liquid chromatography . In: Food Chemistry . tape 107 , no. 3 , 2008, p. 1326-1336 , doi : 10.1016 / j.foodchem.2007.09.037 .
- ↑ a b Wang, Jin; Tang, Feng; Yue, Yongde; Guo, Xuefeng; Yao, Xi: Development and validation of an HPTLC method for simultaneous quantitation of isoorientin, isovitexin, orientin, and vitexin in bamboo-leaf flavonoids . In: Journal of AOAC International . tape 93 , no. 5 , 2010, p. 1376-1383 ( ingentaconnect.com ).
- ↑ Nan Wu, Kuang Fu, Yu-Jie Fu, Yuan-Gang Zu, Fang-Rong Chang, Yung-Husan Chen, Xiao-Lei Liu, Yu Kong, Wei Liu, Cheng-Bo Gu: Antioxidant Activities of Extracts and Main Components of Pigeonpea [Cajanus cajan (L.) Millsp.] Leaves . In: Molecules . tape 14 , no. 3 , 2009, p. 1032-1043 , doi : 10.3390 / molecules14031032 .
- ↑ ML Zeraik, JH Yariwake: Quantification of isoorientin and total flavonoids in Passiflora edulis fruit pulp by HPLC-UV / DAD . In: Microchemical Journal . tape 96 , no. 1 , 2010, p. 86-91 , doi : 10.1016 / j.microc.2010.02.003 .

