Isopropyl thioxanthones
The isopropyl thioxanthones ( ITX ) are heterocyclic organic chemical compounds known as photo-initiator (polymerization) in UV offset printing are used. Usually a mixture of 2- and 4-isopropylthioxanthone is used.
Representative
| Isopropyl thioxanthones | ||||||
| Surname | 1-isopropyl thioxanthone |
2-isopropyl thioxanthone |
3-isopropyl thioxanthone |
4-isopropyl thioxanthone |
||
| other names | 1-ITX |
|
3-ITX |
|
||
| Structural formula |
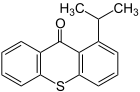
|

|

|

|
||
| CAS number | 5495-84-1 | 83846-86-0 | ||||
| 75081-21-9 (mixture of 2- and 4-isopropylthioxanthone) | ||||||
| PubChem | 79633 | 158403 | ||||
| Molecular formula | C 16 H 14 OS | |||||
| Molar mass | 254.35 g mol −1 | |||||
| Physical state | firmly | |||||
| Brief description | colorless to slightly yellow powder | |||||
| Melting point | 62-77 ° C | 110-111 ° C | ||||
| solubility | insoluble in water, soluble in non-polar organic solvents |
|||||
|
GHS labeling |
|
|
||||
| H and P phrases | no H-phrases | 302-413 | ||||
| no EUH phrases | no EUH phrases | |||||
| no P-phrases | no P-phrases | |||||
| Toxicological data | 348 mg kg −1 ( LD 50 , rat , oral ) | |||||
Health effect
In autumn 2005, baby milk products from Nestlé and Milupa were found in Italy that contained ITX in their Tetra Pak packaging. In the opinion of the Federal Institute for Risk Assessment (BfR), residues of the dye fixer have been transferred from the outside to the inside of the packaging when it is rolled up. Tests showed that no risk of genetic changes caused by ITX is to be expected. The manufacturers Tetra-Pak and Elopak have declared that they have not used ITX in production since 2005.
The American Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) has classified ITX as a highly polluting chemical that is toxic to aquatic organisms . According to a 1999 US study, workers exposed to ITX developed head and neck rashes when exposed to sunlight. Its use in the food sector is therefore controversial. The Federal Institute for Risk Assessment (BfR), however, does not consider it appropriate to replace ITX in printing inks because, with the exception of ITX, a toxicological assessment of the photoinitiators used is currently not possible. For ITX, data are available from which it can be derived that the substance has no genotoxic potential and can therefore be regarded as harmless to health in the event of a transfer of up to 50 micrograms per kilogram (μg / kg) of food.
Analytical studies
An analytical method for determining the isopropylthioxanthone content of milk, yoghurt and fat has been described using the internal standard 2,4-diethylthioxanthone.
See also
Web links
- Bavarian State Office for Health and Food Safety: Contamination of food with isopropylthioxanthone (ITX) - test results 2006–2008
- Statement of the BfR (Federal Institute for Risk Assessment): Components of printing inks in beverages from cardboard packaging (PDF, 37 kB)
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c Entry on 2-isopropylthioxanthone. In: Römpp Online . Georg Thieme Verlag, accessed on May 4, 2014.
- ↑ Bavarian State Office for Health and Food Safety: Isopropylthioxanthone (ITX) , accessed on May 14, 2017.
- ↑ a b c data sheet 4-isopropylthioxanthones from Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on May 14, 2017 ( PDF ).
- ↑ Data sheet 2-isopropylthioxanthones from Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on May 14, 2017 ( PDF ).
- ↑ Statement of the BfR (Federal Institute for Risk Assessment): Replacement of isopropylthioxanthone (ITX) in printing inks with substances that have not been assessed is not appropriate (PDF, 81 kB).
- ↑ Gertrud Morlock and Wolfgang Schwack: Determination of isopropylthioxanthones (ITX) in milk, yoghurt and fat by HPTLC-FLD, HPTLC-ESI / MS and HPTLC-DART / MS . In: Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry . tape 385 , no. 3 , June 2006, p. 586-595 , doi : 10.1007 / s00216-006-0430-5 .
