Johannes Kirchring (the elder)
Johannes Kirchring , also called the Elder (* in Riga ; bl. 1592–1633 in Oldenburg in Oldenburg ), was a German typist and arithmetic master.
Life
Not much is known about Kirchring's life. He signed as Johanne [s] Kirchringk Rigensem Güldenschreiber and arithmetic master zu Oldenburg. It can be assumed that he comes from a branch of the Kerkring family who came to Riga .
His first surviving work for Count Johann VII of Oldenburg and Delmenhorst began in 1592; from then on he worked as a scribe at the Oldenburger Hof. From the year 1598 an invoice from the count's renting company has been received, according to which he received the amount of 28 gr. For two books . In 1620 he was again appointed head of the writing and arithmetic school in Oldenburg by Count Anton Günther von Oldenburg and Delmenhorst . In 1630 he can be verified as living in his son's house, and in 1633 he was still copying roles for the city council.
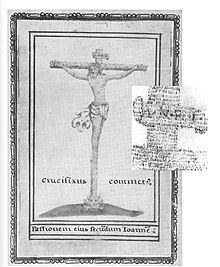
His special gifts included pages designed as micrographs as calligrams . An example of this is the first sheet (fol. 1 r ) in the family register dated 1605 for David von Mandelsloh. It shows a crucifix, the body of which consists of the Latin text of the Passion story according to the Gospel of John , which can only be recognized under a magnifying glass .
His son of the same name, Johannes Kirchring (the younger) ( pp. 1630–1645), was also active as a graphic artist and painter. The Complete Hymnbook written in 1637 in the estate of the Brothers Grimm is more likely to be attributed to him than to his father .
Preserved works
- The Psalter of David with brief summaries and prayers for the house fathers and their children. ( Nikolaus Selnecker ), written 1592 to 1600 for Count Johann VII. (Oldenburg), by inheritance to the Aldenburg-Bentinck house , which it owned until after 1945, auctioned in 1994 at Sotheby’s and 2010 at Christie's .
- Morning and evening prayers , written in 1599, came with the library of Luise Ulrike von Prussia to Sweden in the library of Drottningholm Palace ; since 1854 in the Royal Library in Stockholm .
- The Psalter of the Royal Prophet David , Psalter for Count Anton Günther, 226 sheets of gold and silver writing on parchment, written in 1604, today in the State Museum Oldenburg
- Studbook for David von Mandelsloh , written in 1605, in the Lübeck City Library since the 19th century
- Family and prayer book for Duke Alexander of Schleswig-Holstein-Sonderburg , 132 sheets on parchment, written in 1606, formerly in the Abbey and Gymnasium Library Quedlinburg , came with the Abbey Library in 1938 to Halle (Saale) in what is today the University and State Library of Saxony- Stop .
Web links
Individual evidence
- ↑ guldenschreiber , m . In: Jacob Grimm , Wilhelm Grimm (Hrsg.): German dictionary . 16 volumes in 32 sub-volumes, 1854–1960. S. Hirzel, Leipzig ( woerterbuchnetz.de ). from the 15th to the 17th century often as a title for writers, typists and arithmetic teachers; originally illuminist , lat. aurigraphus , someone who writes or illuminates with gold; not guild writers
- ↑ After Kurt Rastede: The penetration of the high German written language in Oldenburg . In: Oldenburger Jahrbuch of the Association for Regional History and Archeology , 38, 1934, p. 98
- ↑ Johannes Kirchring (the younger) . In: Hans Vollmer (Hrsg.): General lexicon of fine artists from antiquity to the present . Founded by Ulrich Thieme and Felix Becker . tape 20 : Kaufmann – Knilling . EA Seemann, Leipzig 1927, p. 366 .
- ^ Ralf Breslau: The estate of the Brothers Grimm: Catalog. (Catalogs of the manuscript department. Staatsbibliothek zu Berlin Preußischer Kulturbesitz. 2, bequests ISSN 0342-3972 Volume 3) Harrassowitz, Wiesbaden 1997, ISBN 978-3-447-03857-7 , p. 79 (Nachl. Grimm 113)
- ^ Western Manuscripts and Miniatures 1994, lot 83, catalog p. 70
- ↑ Sale 7915, Lot 18 , description at Christie's
- ↑ (Kungliga bibliotekets) handlingar , 7, 1884, p. 24, books.google.com
- ↑ Signature LMO 11.654; see Siglinde Killisch: Oldenburg: cultural history of a historical landscape. (Catalogs of the Landesmuseum Oldenburg 8). Landesmuseum, Oldenburg 1998, ISBN 978-3-89598-533-1 , p. 231
- ↑ Willibald Leo von Lütgendorff-Leinburg (ed.): Das Stammbuch Davids v. Mandelsloh. A contribution to the nobility history of the 17th century. Publishing house and printer (formerly JF Richter), Hamburg 1893. Digitized ; Today's signature: Ms. hist. 8 ° 24
- ↑ catalog entry ; Description in: Jutta Fleige: The manuscripts of the former collegiate and grammar school library Quedlinburg in Halle. Halle 1982, p. 31
| personal data | |
|---|---|
| SURNAME | Kirchring, Johannes |
| ALTERNATIVE NAMES | Kirchring, Johannes the Elder (full name) |
| BRIEF DESCRIPTION | German typist and mathematician |
| DATE OF BIRTH | 16th Century |
| PLACE OF BIRTH | Riga |
| DATE OF DEATH | 17th century |
| Place of death | Oldenburg (Oldenburg) |