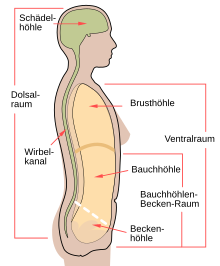
Body cavity
A body cavity is a cavity within the body. In the narrower sense, only the cavities that arise from the section of the coelom located within the embryo (intraembryonic) are referred to as body cavities ( cavitates , singular cavitas ). These are lined with a tunica serosa (short: serosa). The term “cave” is actually misleading, because these caves are filled with internal organs to such an extent that only a capillary gap remains, so a cave only arises when the organs are removed ( evisceration ).
structure
While in fish a uniform body cavity is still formed, in mammals the body cavity lined by a tunica serosa is further subdivided. The thoracic cavity ( Cavitas thoracica ) is embryonic divided from the abdominal cavity ( Cavitas abdominis ) by the diaphragm that is created . The peritoneal cavity is in an open connection to the pelvic cavity ( cavitas pelvis ) towards the rear (in an upright position as in humans, downwards ).
Chest cavity
The thoracic cavity ( Cavitas thoracis, also thoracic space ) is delimited from the outside by the ribs , the thoracic spine and the sternum . At the bottom (in animals behind) the chest cavity is closed by the diaphragm , while there is no sharp border to the neck region towards the head. There are three subspaces within the chest cavity:
- The two pleural cavities ( Cavitates pleurales ), in which the two lungs are located. They are separated by the pleura or pleura .
- The mediastinum ( middle layer ) lies between the two pleural cavities and includes the other organs and connecting paths. These include the heart in the pericardium and the thymus as independent organs as well as the esophagus , trachea , bronchi and the large blood and lymph vessels close to the heart as connecting paths.
Abdominal and pelvic cavities
The abdominal and pelvic space is bounded by the outer abdominal muscles , the lumbar spine , the bony pelvic ring and upwards by the lower edge of the diaphragm . Here, a thin membrane that separates the peritoneum ( peritoneum ), the peritoneal cavity ( peritoneal cavity ), which in a belly portion ( peritoneal cavity abdominis ) and a pelvic part ( peritoneal cavity pekivs may be shared). Outside this peritoneal cavity there is a retroperitoneal part .
In humans, the stomach , spleen , liver , gall bladder , small intestine , ovaries and most of the large intestine are located in the peritoneal cavity (intraperitoneally) . The adrenal glands , pancreas , ureters and a small part of the large intestine are located in the retroperitoneal space. The urinary bladder , prostate , vesicle gland , cervix , vagina and rectum are located in the retroperitoneum of the pelvis .
Individual evidence
- ^ Theodor H. Schiebler, Walter Schmidt, Karl Zilles: Anatomy: cytology, histology, history of development, macroscopic and microscopic human anatomy . 6th edition. Springer, Berlin 2013, ISBN 978-3-662-05731-5 , pp. 485 .
- ↑ a b c d Michael Schünke: Prometheus - learning atlas of anatomy: internal organs . Georg Thieme, Stuttgart 2009, ISBN 978-3-13-139532-0 , p. 2-9 .