Levocetirizine
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
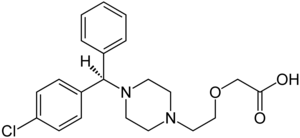
|
||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||
| Non-proprietary name | Levocetirizine | |||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
|||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula |
|
|||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| Drug information | ||||||||||||||||
| ATC code | ||||||||||||||||
| Drug class |
Antihistamine of ethylenediamine -type |
|||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 388,89 g · mol -1 | |||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||||||||
Levocetirizine is a drug from the group of antihistamines that is used for the symptomatic treatment of allergic diseases . Stereochemically , levocetirizine is the active enantiomer ( eutomer ) of cetirizine .
Levocetirizine was first marketed in early 2001 by the Belgian company UCB as an active component of a drug under the name Xusal . The first registration took place in Germany. Levocetirizine was released from the prescription requirement at the end of March 2019.
Clinical information
Application areas (indications)
Levocetirizine is approved for the symptomatic treatment of allergic rhinitis and long-term idiopathic hives .
A superiority over the parent substance cetirizine in terms of efficacy has not yet been clearly proven for levocetirizine due to the lack of comparative studies, even if individual studies suggest this.
Adverse effects (side effects)
- Common: headache, somnolence , dry mouth, tiredness.
- Uncommon: fatigue, abdominal pain.
- Rare: Hypersensitivity reactions including anaphylaxis , dyspnoea , nausea, Quincke's edema , itching, rash, urticaria , weight gain, palpitations , visual disturbances, hepatitis , increased liver function tests, aggressiveness, agitation, epileptic fits , muscle pain.
Trade names
Levocetirizine is the active component of the following drugs: Xusal ( DE ), Xyzall ( AT ), Xyzal ( CH ) and various generics (D, A, CH).
Web links
Individual evidence
- ↑ This substance has either not yet been classified with regard to its hazardousness or a reliable and citable source has not yet been found.
- ↑ Medical Review NDA 22-064. Levocetirizine . (PDF; 1 MB) US Food and Drug Administration, 2007; Retrieved September 25, 2008.
- ↑ Julia Borsch: First OTC levocetirizine preparations available soon. April 16, 2019, accessed July 2, 2020 .
- ↑ GM Walsh: A review of the role of levocetirizine as an effective therapy for allergic disease. In: Expert Opin Pharmacother , Volume 9, 2008, pp. 859-867, PMID 18345961 .
- ↑ C. Bachert: Levocetirizine vs. Cetirizine: An evidence-based differentiation based on pharmacology and clinic. In: Allergology. Volume 29, 2006, pp. 268-273.