Ethylenediamine
| Structural formula | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
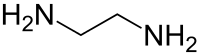
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| General | |||||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Ethylenediamine | ||||||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 2 H 8 N 2 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
colorless liquid with an ammonia-like odor |
||||||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| properties | |||||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 60.10 g mol −1 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
liquid |
||||||||||||||||||
| density |
0.90 g cm −3 (20 ° C) |
||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
8 ° C |
||||||||||||||||||
| boiling point |
116 ° C |
||||||||||||||||||
| Vapor pressure |
|
||||||||||||||||||
| pK s value |
6.90 (pK S1 ) and 9.95 (pK S2 ) for the doubly protonated molecule |
||||||||||||||||||
| solubility |
|
||||||||||||||||||
| Refractive index |
1.4565 (20 ° C) |
||||||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| Authorization procedure under REACH |
Of particular concern: Serious effects on human health are considered likely |
||||||||||||||||||
| MAK |
|
||||||||||||||||||
| Toxicological data | |||||||||||||||||||
| Thermodynamic properties | |||||||||||||||||||
| ΔH f 0 |
−63.0 kJ / mol |
||||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . Refractive index: Na-D line , 20 ° C | |||||||||||||||||||
Ethylenediamine (according to IUPAC nomenclature: ethane-1,2-diamine , often abbreviated as EDA ) is an organic-chemical compound from the group of aliphatic primary amines . More precisely, it is a diamine.
Extraction and presentation
There are several processes and process variants in the chemical industry for the large-scale production of ethylene diamine .
The process most frequently used today for the synthesis of ethylenediamine is the reaction of monoethanolamine with ammonia at temperatures of 160–230 ° C and pressures of 150–250 bar in the presence of hydrogen over transition metal oxide catalysts , which essentially consist of nickel and copper oxide , as well as made of zirconium dioxide and are supported on aluminum oxide (Al 2 O 3 ) in the liquid phase.
The reaction is preferably carried out in fixed bed reactors . Tube reactors and tube bundle reactors , in which molten salts keep the entire reaction at a virtually constant temperature, are particularly suitable for this purpose . In addition to ethylene amine, this process also produces other by-products such as diethylenetriamine (DETA) and triethylenetetramine (TETA), which have to be separated off under pressure by multi-stage distillation work-up. Instead of monoethanolamine , ethylene glycol can preferably also be used. However, ammonia must be used in a two-fold molar excess.
A second large-scale process for the production of ethylenediamine relates to the reaction of 1,2-dichloroethane with ammonia under pressure at 180 ° C. in an aqueous medium. As catalysts also be copper or nickel contacts , as the fixed bed are disposed, is used.
In this case, forms hydrogen chloride , which is present initially as the hydrochloride of the amine in bound form. The amine is converted into its free form by adding sodium hydroxide and can then be recovered from the mixture by rectification . Diethylenetriamine (DETA) and triethylenetetramine (TETA) are also formed as by-products .
properties
Physical Properties
Ethylenediamine has a relative gas density of 2.07 (density ratio to dry air at the same temperature and pressure ) and a relative density of the vapor-air mixture of 1.01 (density ratio to dry air at 20 ° C and normal pressure ). The density is 0.90 g cm −3 at 20 ° C. Ethylenediamine also has a vapor pressure of 12.4 hPa at 20 ° C, 22.6 hPa at 30 ° C, 39.4 hPa at 40 ° C and 66.3 hPa at 50 ° C.
Chemical properties
Ethane-1,2-diamine is a flammable liquid belonging to the group of aliphatic primary amines . It is completely miscible with water and forms a hydrate in the process . The aqueous solutions of ethylenediamine have a strongly basic reaction . In addition, diaminoethane is hygroscopic and smokes in moist air. Ethylenediamine is considered to be of medium to low volatility . An aqueous solution with a concentration of 100 g · l −1 has a pH value of 12.2 at 25 ° C.
use
In complex chemistry, ethylenediamine is particularly used for the synthesis of chelating agents (e.g. ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid ). It is also used as a solvent , stabilizer and for acid neutralization in oils . It is also used in the manufacture of synthetic resins, rubber chemicals, pharmaceuticals, pesticides, inhibitors and detergents and cleaning agents. In organic chemistry , ethylenediamine is also used as a base for the isomerization of allyl alcohols into aldehydes , for the reduction of nitroarenes to azo compounds and many other reactions. It is also used as an intermediate in the areas of corrosion protection , polyamide resins, and lubricant and fuel additives .
safety instructions
Ethylenediamine vapors can form explosive mixtures with air when heated above the flash point. Ethylenediamine is mainly absorbed through the respiratory tract and the skin . This leads to acute irritating effects on the skin and mucous membranes, including burns . A sensitizing effect on the skin and the respiratory tract was also found. Ethylenediamine also has strong effects on the blood , kidneys and cardiovascular system of the person affected. Chronic ingestion or absorption can lead to irritation of the respiratory tract and asthma , the course of which is often unknown. In addition, irritative and allergic skin diseases can develop. An influence on the liver and kidney function was determined in animal experiments . A reproductive toxicity , mutagenicity or carcinogenicity has not yet been proven. Ethylenediamine has a lower explosion limit of about 2.5% by volume and an upper explosion limit of about 16.3% by volume. The ignition temperature is around 400 ° C. The substance therefore falls into temperature class T2 and explosion group IIA. The limit gap width was determined to be 1.25 mm. With a flash point of 34 ° C, ethylene diamine is considered flammable.
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p Entry on ethylene diamine in the GESTIS substance database of the IFA , accessed on March 9, 2019 (JavaScript required)
- ^ DH Ripin, DA Evans: pKa's of Inorganic and Oxo-Acids ( English , PDF) Retrieved July 15, 2014.
- ↑ a b Entry on ethylenediamine. In: Römpp Online . Georg Thieme Verlag, accessed on March 9, 2019.
- ↑ David R. Lide (Ed.): CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics . 90th edition. (Internet version: 2010), CRC Press / Taylor and Francis, Boca Raton, FL, Physical Constants of Organic Compounds, pp. 3-232.
- ↑ Entry on Ethylenediamine in the Classification and Labeling Inventory of the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA), accessed on March 9, 2019. Manufacturers or distributors can expand the harmonized classification and labeling .
- ↑ Entry in the SVHC list of the European Chemicals Agency , accessed on August 11, 2018.
- ↑ Swiss Accident Insurance Fund (Suva): Limit values - current MAK and BAT values (search for 107-15-3 or 1,2-diaminoethane ), accessed on September 15, 2019.
- ↑ David R. Lide (Ed.): CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics . 90th edition. (Internet version: 2010), CRC Press / Taylor and Francis, Boca Raton, FL, Standard Thermodynamic Properties of Chemical Substances, pp. 5-23.
- ↑ a b Patent WO2018224321 : Process for the production of ethylene amines. Published on December 13, 2018 , applicant: BASF SE, inventor: Regine Helga Bebensee, Thomas Heidemann, Barbara Becker, Eva Koch, Hermann Luyken, Johann-Peter Melder.
- ↑ a b Hans-Jürgen Arpe: Industrial organic chemistry - important preliminary and intermediate products . 6th edition. WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim 2007, ISBN 978-3-527-31540-6 , p. 245 .
- ↑ Ethylenediamine (EDA). In: BASF product search. BASF SE, 2014, accessed on March 9, 2019 (German, English).



