Lipanum
The Lipanum is an office and commercial building in Leipzig on Martin-Luther-Ring, the southwestern part of Leipzig's inner city ring . The building is a historical monument.
Building description
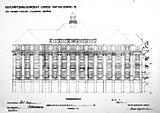
The 59 meter long street front of the four-story building has 14 window axes . Symmetry prevails over 13 axes, the 14th creates the diagonal connection to the northern neighboring building behind the front. The central seven axes are set back slightly on three upper floors and divided by six columns, the rest by pillars. Stone balustrades stand in front of the windows on the first floor . A strong architrave with relief depictions of festoons and rams' heads is located above the third floor . Via the massively enhanced first attic a five-axis configuration with stone vases between the windows, which a rises in the central part walmartigen roofline of a temple-like roof turret is crowned.
The three outer of the thirteen axes are continued in the rear part of the building in two side wings of different lengths, the length of which is limited by the Pleißemühlgraben , which runs open behind the building . An enclosed pedestrian crossing on the second floor leads from a central wing, one floor lower, to a parking garage on the other side of the Pleißemühlgraben.
The Lipanum has 7300 m² of office and retail space.
history
In 1787 the merchant Erdmann Traugott Reichel (1748–1832) acquired the former Apelschen Garten and built several residential buildings on the site, one of them, the so-called front building with 41 window axes, from 1789 to 1792 directly on the street. Felix Mendelssohn Bartholdy (1809–1847) lived here from 1835 to 1836 . Access to the rear buildings was initially through a house passage. When this was replaced by a street in 1890/1891, almost half of the Reichel house had to give way. In 1914 the remaining part of the front building was also removed for the construction of a new office building. The architect was Peter Dybwad (1859–1921), co-builder of the Imperial Court building . It was his last big project.
The bank Knauth, Nachod & Kühne was one of the first tenants in the building, which was completed in 1915 . Another was Otto Beyer , a leading publisher in the field of women's magazines , which later moved to Elsterstrasse and which, after its expropriation in 1946, became the Verlag für die Frau .
After the Second World War, office departments of the VEB Geophysik and the mechanical engineering combine TAKRAF were located in the building . In 1969, the independent again become attracted Handelshochschule one of its sections with a majority. Before it was closed and re-established in 1992, it returned the rooms to the city of Leipzig, which was now the owner of the house. A comprehensive renovation took place in 1995/96. Only now did the building receive the name "Lipanum".
literature
- Wolfgang Hocquél : Leipzig - Architecture from the Romanesque to the present . 1st edition. Passage-Verlag, Leipzig 2001, ISBN 3-932900-54-5 , p. 136 .
Web links
- The Lipanum on Martin-Luther-Ring. Retrieved July 21, 2017 .
- Commercial college; Lipanum. In: Catalog of the Leipzig industrial culture. Retrieved July 21, 2017 .
Individual evidence
- ↑ List of cultural monuments in Leipzig center (ID 09290414)
- ↑ The Lipanum in the heart of Leipzig. Retrieved July 21, 2017 .
Coordinates: 51 ° 20 ′ 16 ″ N , 12 ° 22 ′ 14 ″ E