Magnesium diboride
| Crystal structure | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
||||||||||||||||
| __ Mg __ B | ||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Magnesium diboride | |||||||||||||||
| other names |
Magnesium boride |
|||||||||||||||
| Ratio formula | MgB 2 | |||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
odorless dark gray to black powder |
|||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 45.93 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
|||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
800 ° C (decomposition) |
|||||||||||||||
| solubility |
almost insoluble in water |
|||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||||||||
Magnesium diboride is an intermetallic compound , which currently has the highest transition temperature (39 K) among the metallic superconductors . This is almost a doubling of the previously known leader ( niobium germanium , Nb 3 Ge, at 23 K). This property was only discovered by the Japanese scientist Jun Akimitsu in 2001 , although magnesium diboride has been known and easy to manufacture for over 50 years (but not in its pure form).
Extraction and presentation
As early as 1914 there was a report on the preparation of a magnesium boride, which was created by heating amorphous, finely divided boron with magnesium powder until it was red hot in a hydrogen stream. The same compound was observed in the reaction of magnesium with boron trioxide in addition to magnesium oxide .
Production of pure magnesium diboride
The production of pure magnesium diboride, as it is required for superconductors, is complex. Since magnesium melts at 650 ° C, but boron only melts at over 2000 ° C (where magnesium is already gaseous), it is not possible to produce magnesium diboride by melting it down. Instead, the two starting materials are brought together at 900 ° C, i.e. at a temperature at which magnesium does not yet boil. The magnesium vapor that occurs nevertheless diffuses into the boron, where easily detachable magnesium diboride spheres are formed. Thin wires can be made in a similar process.
It is also possible to deposit thin layers of magnesium diboride by reacting magnesium vapor in a hydrogen atmosphere with diborane .
properties
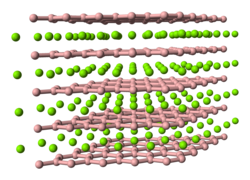
Magnesium diboride is an odorless dark gray to black powder. Studies on magnesium diboride were first published in 1954 by Jones and March. This magnesium boride , which is the most metal-rich one to date (up to the present time , four other binary magnesium borides are known in the literature with MgB 4 , MgB 7 , MgB 12 and MgB 20 ) crystallizes in the aluminum diboride type in the space group P 6 / mmm (space group no.191) and the lattice constants a = 3.0834 (3) Å and c = 3.522 (2) Å. The boron atoms in the ab plane form a graphite-like network of planar edge-linked six-membered rings, the magnesium atoms being located above and below the ring centers and the boron atoms being surrounded by them in a trigonal prismatic manner.
literature
- Paul Canfield, Sergey L. Bud'ko: Hot prospects for cryogenic superconductors . In: Spectrum of Science . No. 6, 2005, p. 56ff.
- Gunnar Moos: On the dynamics of low-energy electrons in metallic solids. Dissertation, FU Berlin 2003 ( Chapter 5: Electron dynamics in magnesium diboride (PDF; 433 kB), urn : nbn: de: kobv: 188-2003000435 ).
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e f data sheet magnesium diboride from AlfaAesar, accessed on February 1, 2013 ( PDF )(JavaScript required) . .
- ↑ Andrea Naica-Loebell: New superconductor magnesium diboride . Telepolis, February 27, 2001, accessed January 16, 2012
- ↑ Andrea Naica-Loebell: The mechanisms of superconductivity in magnesium diboride . Telepolis, June 6, 2001, accessed January 16, 2012
- ↑ a b Ruth Schmitt: Binary and ternary borides of the alkaline earth metals: syntheses, crystal structures and properties . 2006, urn : nbn: de: bsz: 21-opus-22651 (dissertation, University of Tübingen, 2006).
- ↑ Veronika Winkler: Magnesium diboride takes another hurdle - production of high-quality superconducting films . Neue Zürcher Zeitung, September 18, 2002, accessed on September 18, 2014.
