Mashrek
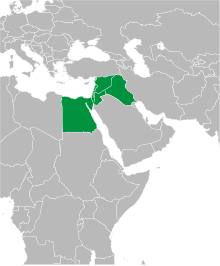
The Maschrek (also Maschrik or Maschriq , Arabic المشرق, DMG al-Mašriq ' Orient ') has been an area in the Middle East since the Arab-Islamic expansion in the 7th century . The Maschrek is not precisely defined politically, but in general it refers to the countries with an Arabic-speaking majority east of Libya and north of Saudi Arabia , specifically the states of Egypt , Palestine , Israel , Jordan , Lebanon , Syria and Iraq .
Word origin
The word arabic المشرق al-Maschrek , DMG al-mašriq is from the verbشَرَقَ sharaqa , DMG šaraqa ‚rise (sun); shine 'derived and literally means "place where the sun rises". In contrast to this is the term Maghreb المغرب, DMG al-maġrib 'place where the sun goes down; the West'. Both geographical names come from the time before the emergence of the Islamic Empire and refer to the division of the world in the late Roman Empire .
Special status of Egypt
Egypt has a special position , on the one hand because of its history and on the other hand because of its location on the African continent . Since the Arab-Islamic conquest, Egypt has belonged culturally and linguistically to Mashreq and is therefore counted among it. It borders on the Maghreb region to the west.
history
During the Arab expansion in the 7th century, the Mashrek was the seat of the Umayyad caliphate . This was initially in Damascus , later he moved to Baghdad . In the following centuries, various, mostly Turkish dynasties ruled the region. The Ottomans ruled the area from 1517 to 1918 . During the First World War , leading Arab politicians initially hoped that the Triple Entente would support their efforts for independence . The Hussein-McMahon correspondence from 1915 to 1916 between Hussein ibn Ali , Sherif of Mecca , and Sir Henry McMahon , the British High Commissioner in Egypt, gave rise to such hopes. In addition, the Arab revolt 1916–1918 against Turkish rule was supported by Great Britain . However, these expectations were dashed by the subsequent division of the region into areas controlled by Great Britain and France under the secret Sykes-Picot Agreement of May 1916. The British zone of influence comprised the League of Nations Mandate for Palestine and the British Mandate Mesopotamia on what is now Iraq , the French zone of influence included the League of Nations mandate for Syria and Lebanon . Hussein ibn Ali was first recognized as king of the Hejaz , but was subject to the rival Saud dynasty in 1924 . Furthermore, in the Balfour Declaration of 1917, the British promised the Jews the establishment of a “national homeland”. The modern borders in Maschrek were drawn by the European Western powers after the fall of the Ottoman Empire .
See also
Individual evidence
-
↑ See Thomas Eich: Maschrek. In: bpb.de . Archived from the original on July 21, 2012 ; accessed on November 23, 2019 . Lorenz Abu Ayyash: Editorial. In: From Politics and Contemporary History (APUZ) 33–34 2016. August 12, 2016, accessed on November 23, 2019 .