Varistor
A varistor is an electrical component that is characterized by a resistance that is dependent on the electrical voltage . Above a certain threshold voltage, which is typical for the respective varistor, the differential resistance becomes abruptly smaller. The polarity of voltage and current does not matter; a rectifier effect as with a diode does not occur. The term varistor is one of the English terms " var iable res istor composite" portmanteau word . A varistor is also known as VDR for Voltage Dependent Resistor , i.e. voltage-dependent resistance. The abbreviation MOV is common for metal oxide varistors.
The main application of a varistor is overvoltage protection , for which purpose it is connected in parallel to the component to be protected.
construction
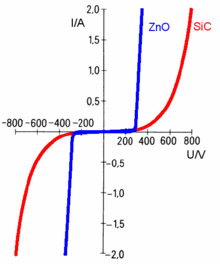
Today varistors are mostly made on the basis of zinc oxide (ZnO). Together with other metal oxides, such as bismuth oxide , chromium oxide or manganese oxide , the powder is pressed and sintered in tablet form . The blank is contacted with silver or aluminum on two sides and provided with connections. In the past, varistors were made from silicon carbide (SiC). These varistors are now considered obsolete, as their current-voltage characteristic curve is significantly flatter above the threshold voltage than with ZnO varistors.
functionality
The zinc oxide varistor consists of many small zinc oxide grains with different conductivity. Barrier layers are created between the zinc oxide grains at the points of contact. An applied voltage creates an electric field that partially degrades the barrier layers. The higher the applied voltage, the more barrier layers are broken down and the resistance decreases. The threshold voltage can be varied via the thickness of the varistor disks: the thicker the varistor disk, the more zinc oxide grains are connected in series and the higher the threshold voltage.
Current-voltage characteristic
The characteristic is given in two types of representation:
- linear (see opposite), in which symmetry and threshold voltage become clear, or
- double logarithmic (see web links), in which characteristic details become clear.
The response voltage , threshold voltage or varistor voltage is usually given in the data sheets as the voltage drop at a current of . This voltage is pretty much at the beginning of the breakdown range in which the protective behavior is effective. The characteristic curve in the breakdown area is approximated by
with and .
The exponent determines the slope of the characteristic. For zinc oxide varistors it is typically in the range 30… 70 or 25… 50, for SiC varistors in the range 3… 7 or 5… 7.
Below the breakdown range, the characteristic curve changes into a leakage current range with currents typically <1 μA. The varistor is operated there as long as it does not protectively intervene. An ohmic component is superimposed above the breakdown area. In this high current range beyond a current surge specified in the data sheet, a varistor may only be operated once.
In continuous operation, a direct voltage and the peak value of an alternating voltage must remain below . In addition, there are a number of voltage values over several powers of ten with a sample spread of 10% in many cases.
Designs

The following designs are most commonly used:
- in disc shape with connecting wires
- as an SMD module
- clipped to contactors
When used in electronic circuits, the size is preferably determined
- in continuous operation by a flow of heat to be delivered electric power
- in the event of individual interference peaks due to the short-term energy to be stored
behavior
The behavior of a varistor in the breakdown region in to an example , , are explained.
- Voltage - current intensity
If the voltage is 10% higher, the current is higher by a factor .
If the current is 10% higher, the voltage is increased by the factor or additively by 2.4 ‰.
If the current strength is 1000 times greater, the voltage is increased by the factor or additively by 19%.
- Large signal resistance
This is the resistance in terms of the total voltage and current.
At 1 mA:
At 1 A:
This means that the large-signal resistance at 1 A is around the factor , i.e. almost three powers of ten, smaller than at 1 mA.
- Small signal resistance
This is the resistance in the event of small changes in voltage and current strength and is equal to the differential resistance .
He arises from
This means that the small-signal resistance is a factor smaller than the large- signal resistance for any current strength in the breakdown range .
application areas
Varistors are suitable for protecting against overvoltages . In normal operation, their resistance is very high, while with overvoltage the resistance becomes very small almost instantaneously and discharges charge . They are used both to protect sensitive electronic circuits and in power engineering. Varistors have response times of less than a nanosecond and can limit brief overvoltages very quickly without being destroyed. If the duration is longer, the varistor overheats because the energy that can be absorbed depends on the total mass.

A disadvantage of ZnO varistors is that they “age” due to several smaller overvoltages, that is, their threshold voltage becomes lower over time and their leakage current increases. In particular, protection ends after a single load in the high-current range. Therefore, you should always operate it with a fuse, for example. B. Avoid fires. SiC varistors did not show this type of aging. Depending on the equipment, surge protective devices can check the operating status and report optically (in the picture opposite by the color in the diamond-shaped window) or by an electrical signal (in the picture by an auxiliary contact behind the green terminals) that the varistor needs to be replaced.
As an alternative to varistors, suppressor diodes are also used in protective circuits . Suppressor diodes are destroyed by low energies in the event of overvoltage, so that they are mainly used for lower voltages, such as those that occur in signal lines, for example. On the other hand, unlike varistors, suppressor diodes do not age. In applications in which high-frequency signals are to be transmitted, the considerably higher capacitance of varistors compared to suppressor diodes can cause impermissible attenuation of the useful signal.
There are also gas discharge tubes and spark gaps as coarse protection elements. These can absorb very large energies in the event of overvoltages, but have a longer response time of up to a few microseconds compared to varistors. That is why they are often used in combination with varistors.
Varistors are also used as (demand) current bridges for the series connection of incandescent lamps in fairy lights .
Web links
- Technical introduction PDF document. Retrieved July 15, 2018.
- Voltage-dependent resistors PDF document (367 KB)
Individual evidence
- ^ A b Erwin Böhmer, Dietmar Ehrhardt, Wolfgang Oberschelp: Elements of applied electronics: Compendium for training and occupation. Vieweg + Teubner, 16th ed., P. 22
- ↑ Michael Reisch: Electronic components: function, basic circuits, modeling with SPICE. Springer, 1998, p. 87
- ↑ a b Michael Reisch: Electronic components: function, basic circuits, modeling with SPICE. Springer, 1998, p. 84 f
- ^ Klaus Ellmer, Andreas Klein, Bernd Rech: Transparent Conductive Zinc Oxide: Basics and Applications in Thin Film Solar Cells . Springer, 2008, p. 54
- ↑ Herbert Tholl: Components of Semiconductor Electronics: Part 2 Field Effect Transistors, Thyristors and Optoelectronics . Teubner, 1978, p. 282
- ↑ Waldemar Münch: Electrical and magnetic properties of matter . Springer / Teubner, 1987, p. 162
- ↑ Data sheet disk varistor. (PDF) Retrieved July 15, 2018 .
- ↑ Data sheet SMD component. (PDF) Retrieved July 15, 2018 .
- ↑ Data sheet industrial type. (PDF) Retrieved July 15, 2018 .
- ↑ Catalog Surge Arresters, p. 3. Accessed on July 18, 2018 .